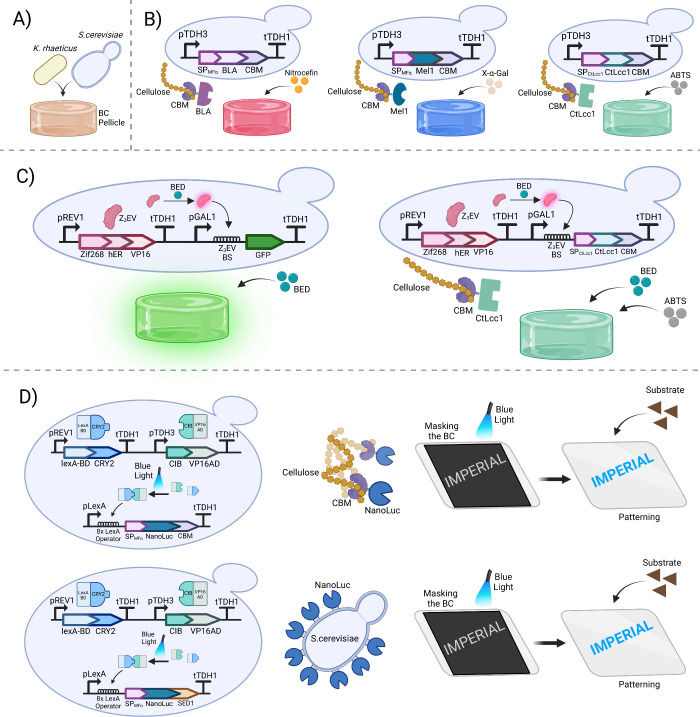
Figure 5.
Functionalized ELMs by a coculture of a BC-producer and yeast. (A) Syn-SCOBY: a synthetic coculture of K. rhaeticus and S. cerevisiae, where yeast converts sucrose to glucose for K. rhaeticus utilization. (B) Functionalization of ELMs with extracellular enzymes: yeast secretes CBM-fused enzymes like β-lactamase (BLA), α-galactosidase (Mel1), and laccase (CtLcc1) to bind cellulose fibers in ELMs, producing specific-colored responses upon substrate addition; red color with BLA and nitrocefin, blue color with Mel1 and X-α-Gal, and dark green color with CtLcc1 and ABTS. MF-α secretion signal peptide (SPMF-α) or native secretion signal peptide (SPCtLcc1) were used to secrete the fused constructs. (C) Estrogen sensor ELM: a human hormone β-estradiol (BED) sensor that activates the Z3EV transcription factor in yeast, triggering GFP or CtLcc1-CBM expression, resulting in green fluorescence or dark green color in response to BED. (D) Optogenetic patterning: a blue-light-inducible system in ELMs activates CRY2-CIB fusion, binding to LexA operators (8x LexA) in the pLexA promoter to activate NanoLuc expression. Upon substrate addition, a blue pattern forms where a blue light is applied.