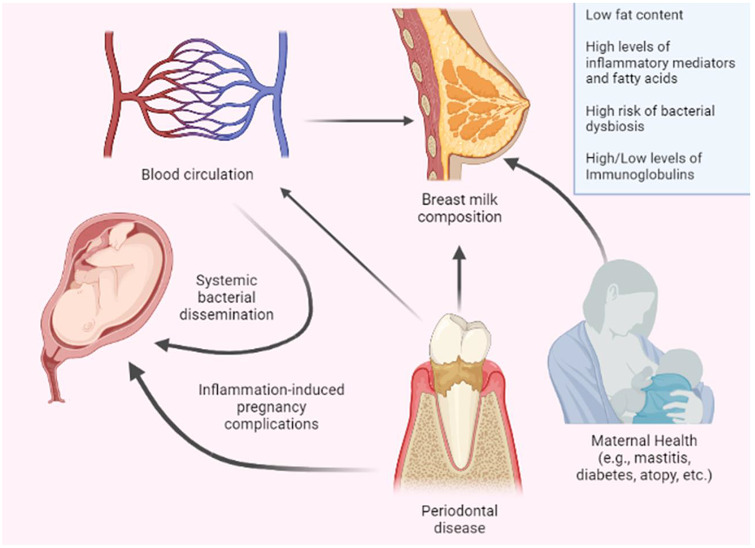
Figure 2.
A simplified diagram showing the potential mechanism explaining the impact of periodontal disease on breast milk composition. Maternal diseases/infections (such as diabetes, mastitis, and atopy) can affect the composition of breast milk. Periodontal diseases have been reported to in the literature to be associated with adverse pregnancy outcomes, including preeclampsia, preterm birth, and low birth weight. Potential biological pathways through which periodontal diseases can negatively affect breast milk composition include the systemic dissemination of inflammatory cytokines like IL-1, IL-6, PGE2, and TNF-β in the blood circulation that can be up-regulated by bacterial by-products. Based on results from this review, it can be hypothesized that milk from mothers with periodontal diseases might have low fat content, high levels of inflammatory mediators and fatty acids, changes in levels of immunoglobulins, and higher risk of bacterial dysbiosis, compared to milk from mothers with good periodontal health. (Prepared using Biorender.com).