FIGURE 5.
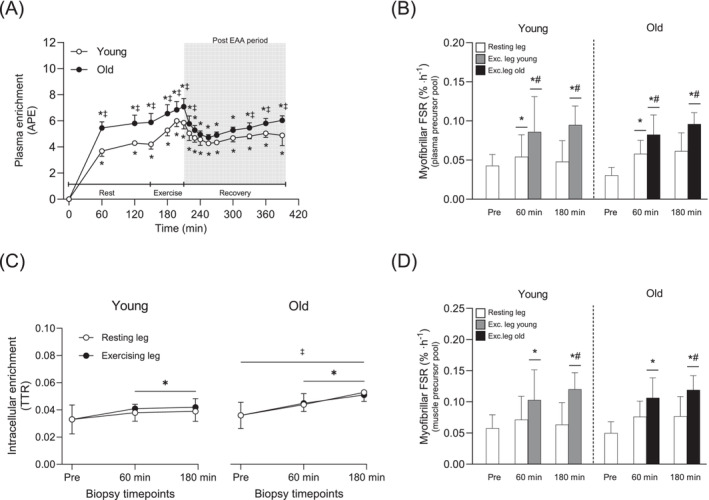
Plasma enrichment of L‐[ring 13C6] phenylalanine during the experimental trial In Young and Old (A), myofibrillar protein fractional synthesis rates (FSR) before and after resistance exercise and intake of EAA in the resting and exercising leg of Young and Old determined using plasma enrichment as the precursor (B), free intracellular enrichment of L‐[ring 13C6] phenylalanine in the resting and exercising leg of Young and Old (C), myofibrillar protein FSR before and after resistance exercise and intake of EAA in the resting and exercising leg of Young and Old determined using free intracellular enrichment as the precursor (D). For plasma variables, white and black circles represent Young and Old, respectively. In muscle, white bars represent the resting leg in both groups, whereas grey and black bars represent the exercising leg in Young and Old, respectively. A two‐way (age × time) repeated‐measures ANOVA was used to analysed plasma enrichment and the ANOVA revealed a significant interaction effect (age × time). A three‐way (age × time × leg) repeated‐measures ANOVA was used to analyse the FSR and the enrichment of the intracellular fraction. The ANOVA revealed a significant interaction effect (time × leg) for (B,D), a significant interaction (age × leg) for (C) and a main effect of time for (C). For plasma, symbols marked without lines represent a two‐way interaction, and symbols marked with a long line represent a main effect. For muscle, symbols marked with short lines represent a two‐way interaction; *p < 0.05 different from baseline, #p < 0.05 different from the resting leg, ‡p < 0.05 different from Young. Values are presented as means ± SD for 20 participants. For statistical analyses, data for (B) and (C) were log‐transformed.
