Fig. 1.
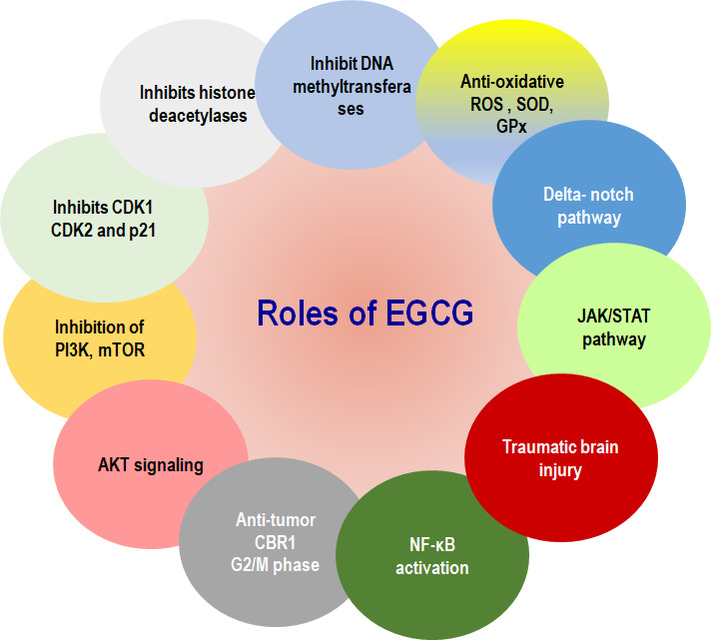
Mechanistic Overview of Modulation of Cellular Signaling Pathways by EGCG. This figure illustrates the multifaceted mechanism of EGCG and its interactions with key signaling and molecular pathways. EGCG is shown to regulate various target genes and proteins, including JAK/STAT, NF-κB, AKT, and Notch pathways, highlighting its critical roles in cellular processes such as apoptosis, proliferation, and survival. The diagram emphasizes the biological functions of EGCG, including its anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant activities. By inhibiting oxidative stress, reducing inflammation, and promoting apoptosis in cancer cells, EGCG showcases its therapeutic potential in combating diseases like cancer, cardiovascular , and neurodegenerative diseases
