Fig. 8.
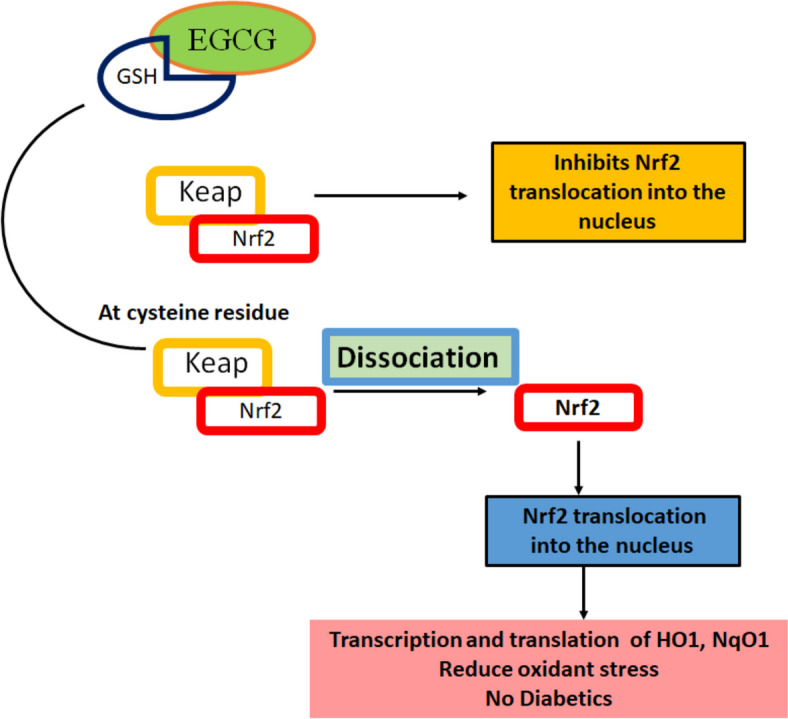
The Role of EGCG in Diabetes Management. Showing the pivotal role of EGCG in diabetes, particularly through its interaction with the KEAP1-Nrf2 signaling pathway. EGCG forms a hybrid complex with glutathione (GSH), which binds to KEAP1, resulting in the dissociation of KEAP1 from Nrf2. This dissociation allows Nrf2 to translocate into the nucleus, where it initiates the transcription of crucial antioxidant proteins, including heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) and NAD(P)H quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1). These antioxidant proteins play an important role in reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, key contributors to diabetic complications
