Abstract
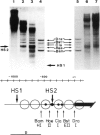
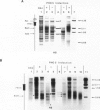
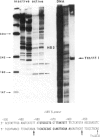
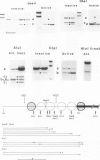
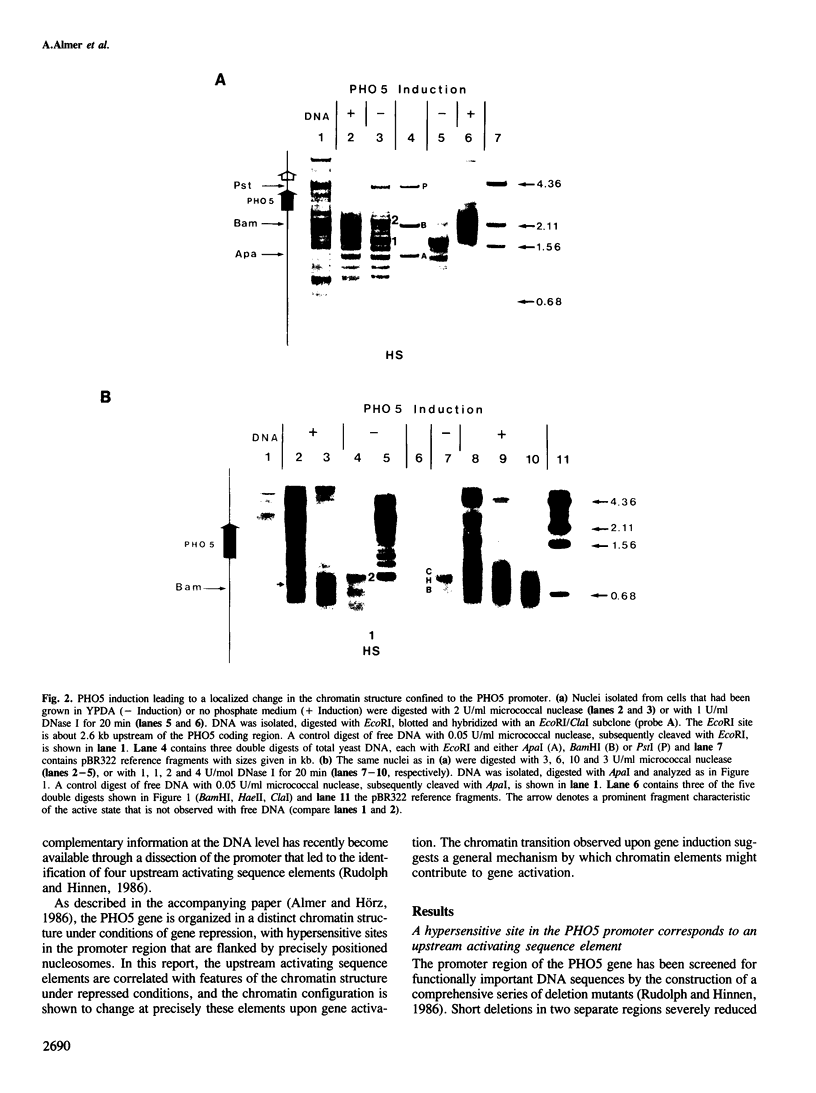
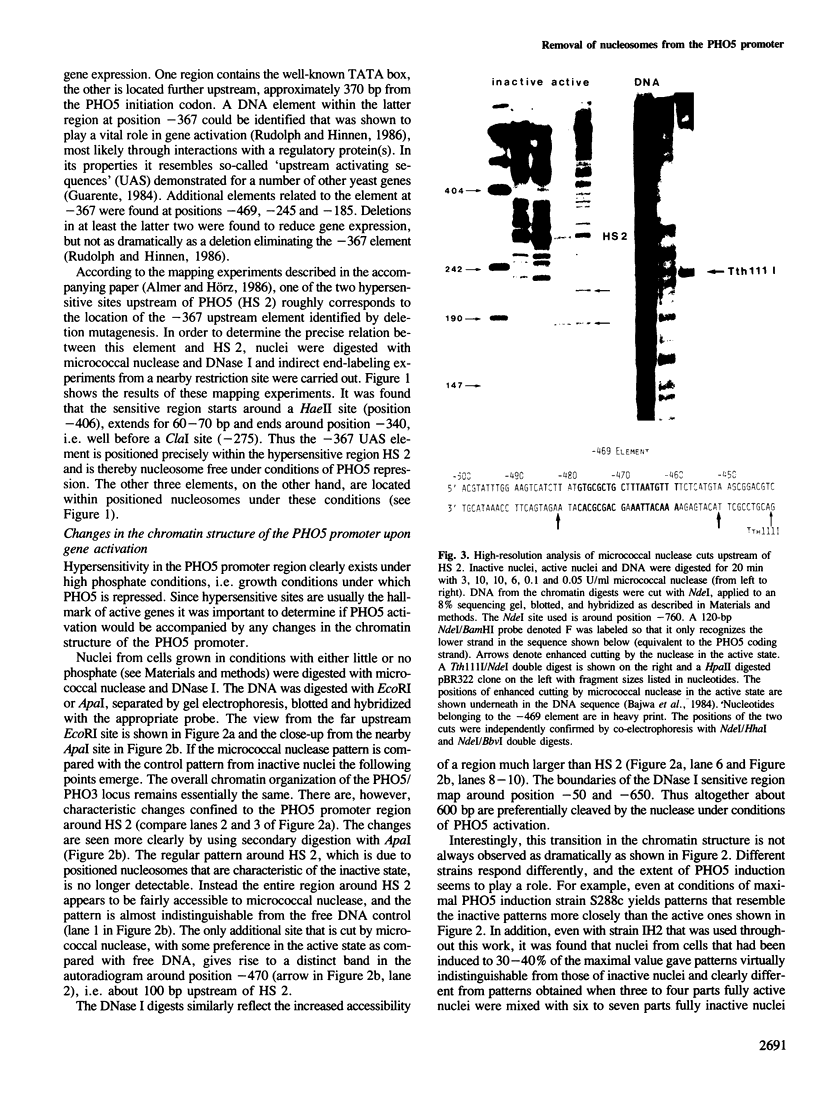
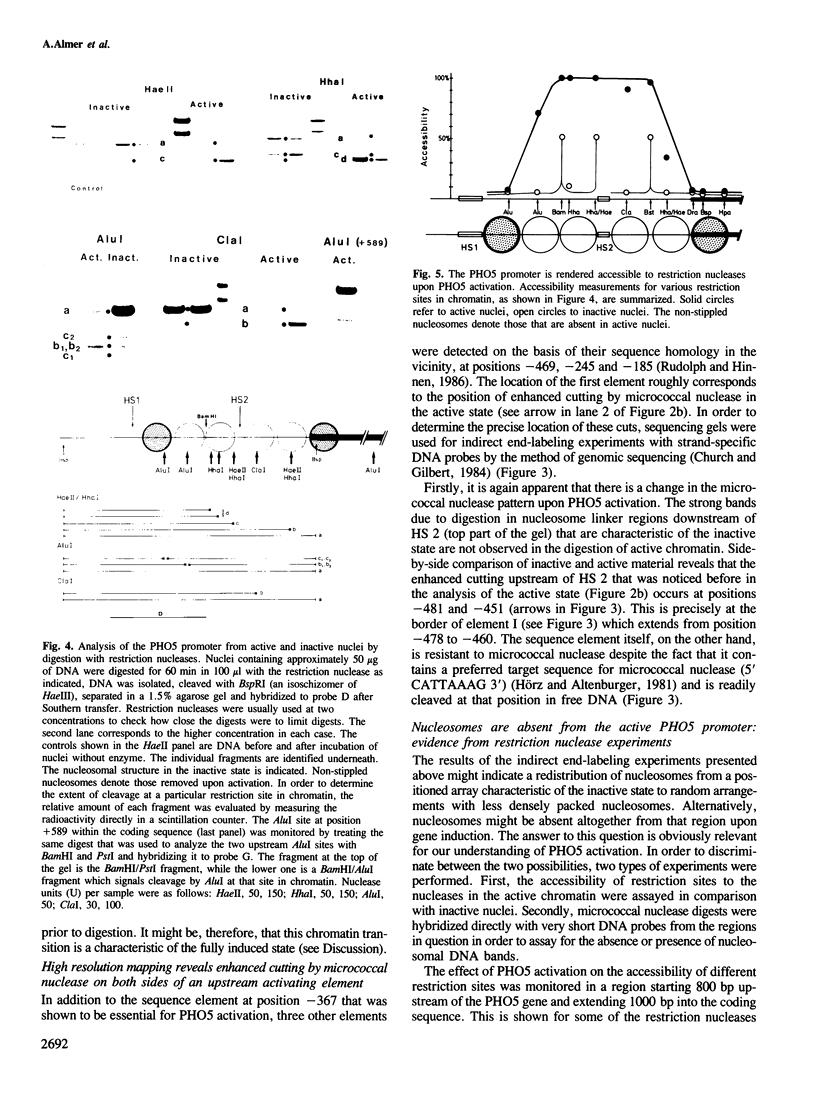
The chromatin fine structure in the promoter region of PHO5, the structural gene for a strongly regulated acid phosphatase in yeast, was analyzed. An upstream activating sequence 367 bp away from the start of the coding sequence that is essential for gene induction was found to reside in the center of a hypersensitive region under conditions of PHO5 repression. Under these conditions three related elements at positions -469, -245 and -185 are contained within precisely positioned nucleosomes located on both sides of the hypersensitive region. Upon PHO5 induction the chromatin structure of the promoter undergoes a defined transition, in the course of which two nucleosomes upstream and two nucleosomes downstream of the hypersensitive site are selectively removed. In this way approximately 600 bp upstream of the PHO5 coding sequence become highly accessible and all four elements are free to interact with putative regulatory proteins. These findings suggest a mechanism by which the chromatin structure participates in the functioning of a regulated promoter.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almer A., Hörz W. Nuclease hypersensitive regions with adjacent positioned nucleosomes mark the gene boundaries of the PHO5/PHO3 locus in yeast. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2681–2687. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04551.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajwa W., Meyhack B., Rudolph H., Schweingruber A. M., Hinnen A. Structural analysis of the two tandemly repeated acid phosphatase genes in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 25;12(20):7721–7739. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.20.7721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman L. W., Kramer R. A. Modulation of chromatin structure associated with derepression of the acid phosphatase gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7223–7227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman L. W., Stranathan M. C., Preis L. H. Structure of the transcriptionally repressed phosphate-repressible acid phosphatase gene (PHO5) of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):38–46. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright I. L., Abmayr S. M., Fleischmann G., Lowenhaupt K., Elgin S. C., Keene M. A., Howard G. C. Chromatin structure and gene activity: the role of nonhistone chromosomal proteins. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1982;13(1):1–86. doi: 10.3109/10409238209108709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C. Anatomy of hypersensitive sites. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):213–214. doi: 10.1038/309213a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C. DNAase I-hypersensitive sites of chromatin. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):413–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90381-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson B. M., Felsenfeld G. Specific factor conferring nuclease hypersensitivity at the 5' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):95–99. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson B. M., Lewis C. D., Felsenfeld G. Interaction of specific nuclear factors with the nuclease-hypersensitive region of the chicken adult beta-globin gene: nature of the binding domain. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90057-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field C., Schekman R. Localized secretion of acid phosphatase reflects the pattern of cell surface growth in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jul;86(1):123–128. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritton H. P., Igo-Kemenes T., Nowock J., Strech-Jurk U., Theisen M., Sippel A. E. Alternative sets of DNase I-hypersensitive sites characterize the various functional states of the chicken lysozyme gene. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):163–165. doi: 10.1038/311163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giniger E., Varnum S. M., Ptashne M. Specific DNA binding of GAL4, a positive regulatory protein of yeast. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):767–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90336-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L. Yeast promoters: positive and negative elements. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):799–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörz W., Altenburger W. Sequence specific cleavage of DNA by micrococcal nuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2643–2658. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igo-Kemenes T., Hörz W., Zachau H. G. Chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:89–121. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.000513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohr D. Organization of the GAL1-GAL10 intergenic control region chromatin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8457–8474. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis D., Oudet P., Chambon P. Structure of transcribing chromatin. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1980;24:1–55. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60670-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Wood W. I., Dolan M., Engel J. D., Felsenfeld G. A 200 base pair region at the 5' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene is accessible to nuclease digestion. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):45–55. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90359-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyhack B., Bajwa W., Rudolph H., Hinnen A. Two yeast acid phosphatase structural genes are the result of a tandem duplication and show different degrees of homology in their promoter and coding sequences. EMBO J. 1982;1(6):675–680. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01229.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proffitt J. H. DNase I-hypersensitive sites in the galactose gene cluster of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1522–1524. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph H., Koenig-Rauseo I., Hinnen A. One-step gene replacement in yeast by cotransformation. Gene. 1985;36(1-2):87–95. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shermoen A. W., Beckendorf S. K. A complex of interacting DNAase I-hypersensitive sites near the Drosophila glue protein gene, Sgs4. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):601–607. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sledziewski A., Young E. T. Chromatin conformational changes accompany transcriptional activation of a glucose-repressed gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):253–256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Promoter elements, regulatory elements, and chromatin structure of the yeast his3 gene. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):901–910. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H. Assembly and propagation of repressed and depressed chromosomal states. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):705–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90267-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. The 5' ends of Drosophila heat shock genes in chromatin are hypersensitive to DNase I. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):854–860. doi: 10.1038/286854a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. Two protein-binding sites in chromatin implicated in the activation of heat-shock genes. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):229–234. doi: 10.1038/309229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. The locus of sequence-directed and protein-induced DNA bending. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):509–513. doi: 10.1038/308509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]