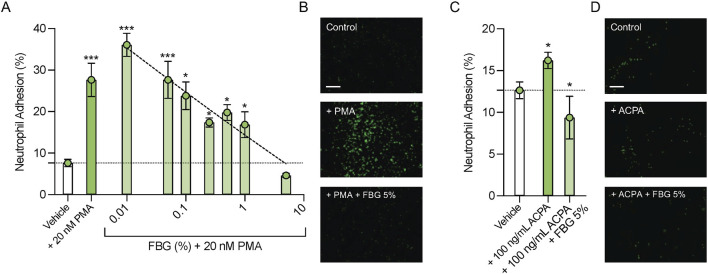
FIGURE 4.
Pooled human immune globulins (Flebogamma® DIF) prevent PMA and H4R3 ACPA induced adhesion to human corneal epithelial cells. (A) Exposure to PMA (20 nM) significantly increased neutrophil adhesion to human corneal epithelial cells compared to Vehicle. Flebogamma® DIF dose-dependently reduced adhesion. 5% Flebogamma® DIF completely prevented the PMA mediated increase in adhesion to corneal epithelial cells. Data were analyzed by One-Way ANOVA with Holm-Šídák multiple comparisons test. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 vs. Vehicle. (B) Representative low magnification bright field fluorescence microscopy images are shown. (C) H4R3 ACPA increased neutrophil adhesion to corneal epithelial cells compared with Vehicle. 5% Flebogamma® DIF reduced adhesion in the presence of H4R3 ACPA to levels below Vehicle. Data were analyzed by Brown-Forsythe ANOVA (P < 0.001) with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. *P < 0.05 vs. Vehicle. (D) Representative low magnification bright field fluorescence microscopy images are shown. Scale bar: 250 µm.