Figure 1.
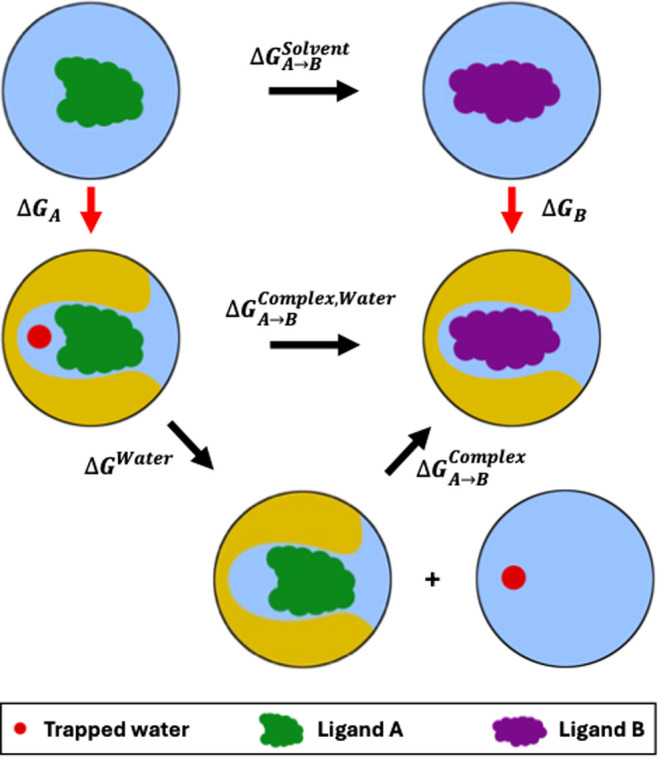
Relative binding free energy (RBFE) calculation between two ligands, where one ligand (ligand A) binds to the protein (yellow) with a trapped water, while the other ligand (ligand B) displaces it. The vertical transformations in red represent absolute binding free energy (ABFE) calculations for the individual ligands binding to the protein. The horizontal lines in black represent the transformations of the ligands in solvent (solvent leg of the RBFE calculation, ΔGSolventA–>B) and in protein’s binding site (complex leg of the RBFE calculation, ΔGComplex,WaterA–>B), the two components of the RBFE calculation. For the complex leg of the RBFE calculation, we use the separation of states approach where we first introduce a new state of the system (bottom) with a binding mode of the ligand A without the trapped water. In this state of the system, the trapped water is displaced from the binding site of the protein into the bulk solvent. From this binding mode of ligand A without the trapped water, we transform the ligand A into another ligand B that is known to displace the trapped water when it binds.
