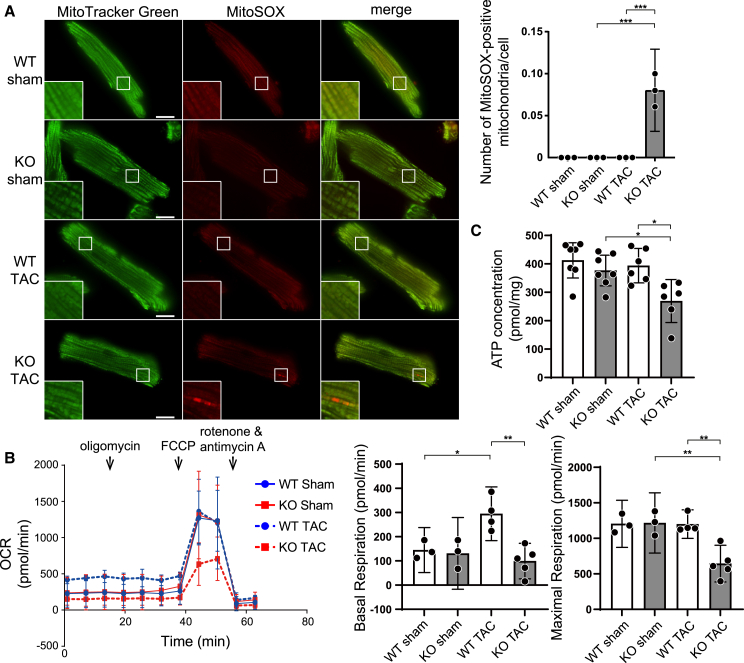
Figure 3.
Mitochondrial dysfunction in TAC-operated Bcl2l13−/− mice
(A) Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in cardiomyocytes. Cardiomyocytes were isolated 5 days after the TAC operation and stained with MitoSOX and MitoTracker Green for confocal microscopy (n = 3). MitoSOX-positive mitochondria in the boxed area are shown at higher magnification in the inset. Scale bar: 10 μm. The number of MitoSOX-positive mitochondria per cell is shown in the bar graph. At least 30 cells were observed in each experiment.
(B) The oxygen consumption rate (OCR) of isolated cardiomyocytes 5 days after TAC was assessed using the Seahorse XF24 extracellular flux analyzer. n = 3 (WT sham), 3 (KO sham), 3 (WT TAC), or 5 (KO TAC) per group. Reagents were injected sequentially during the assay to yield final concentrations of 1 μM oligomycin, 2 μM carbonyl cyanide 4-(trifluoromethoxy) phenylhydrazone (FCCP), 2 μM rotenone, and 4 μM antimycin A. Basal respiration and maximal respiration are shown in the bar graphs.
(C) Tissue ATP levels were measured using the left ventricle from mice 5 days after TAC. n = 7 (WT sham), 7 (KO sham), 6 (WT TAC), or 6 (KO TAC) per group. Results are shown as mean with 95% CI. Statistical analysis by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey-Kramer’s post hoc test. All pairwise comparisons were performed. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.