Abstract
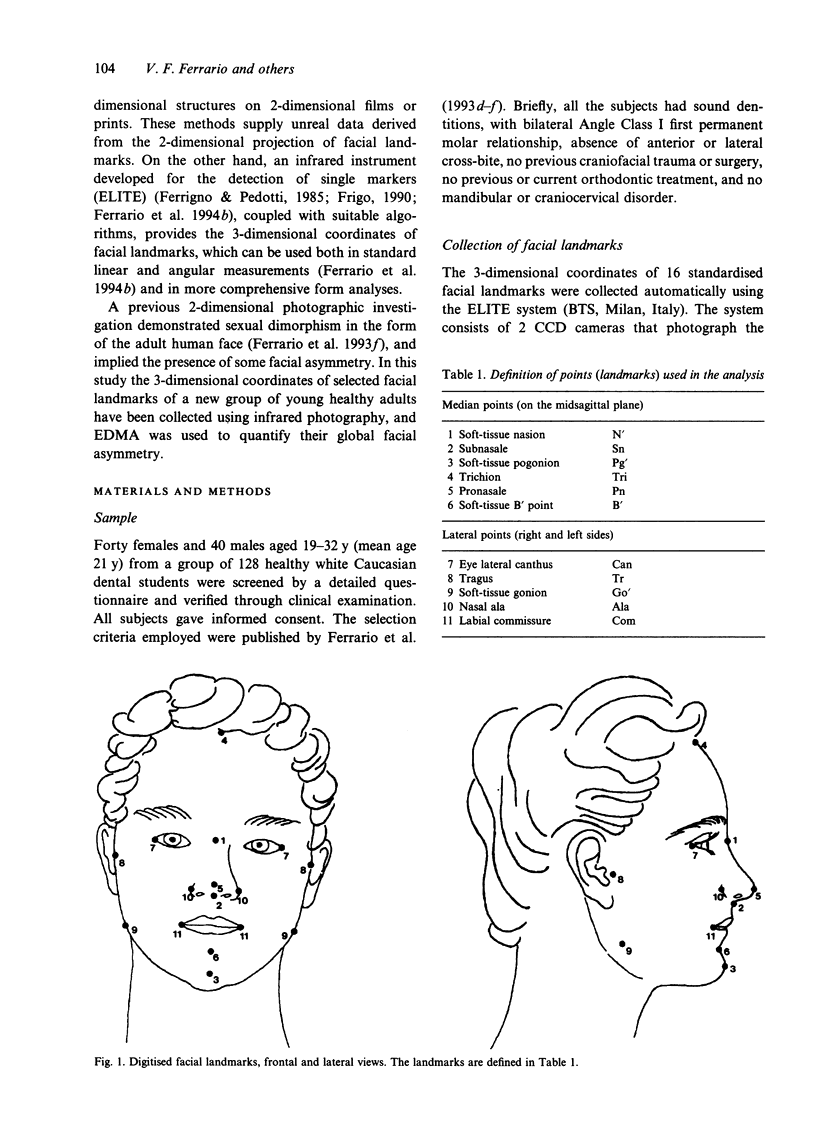
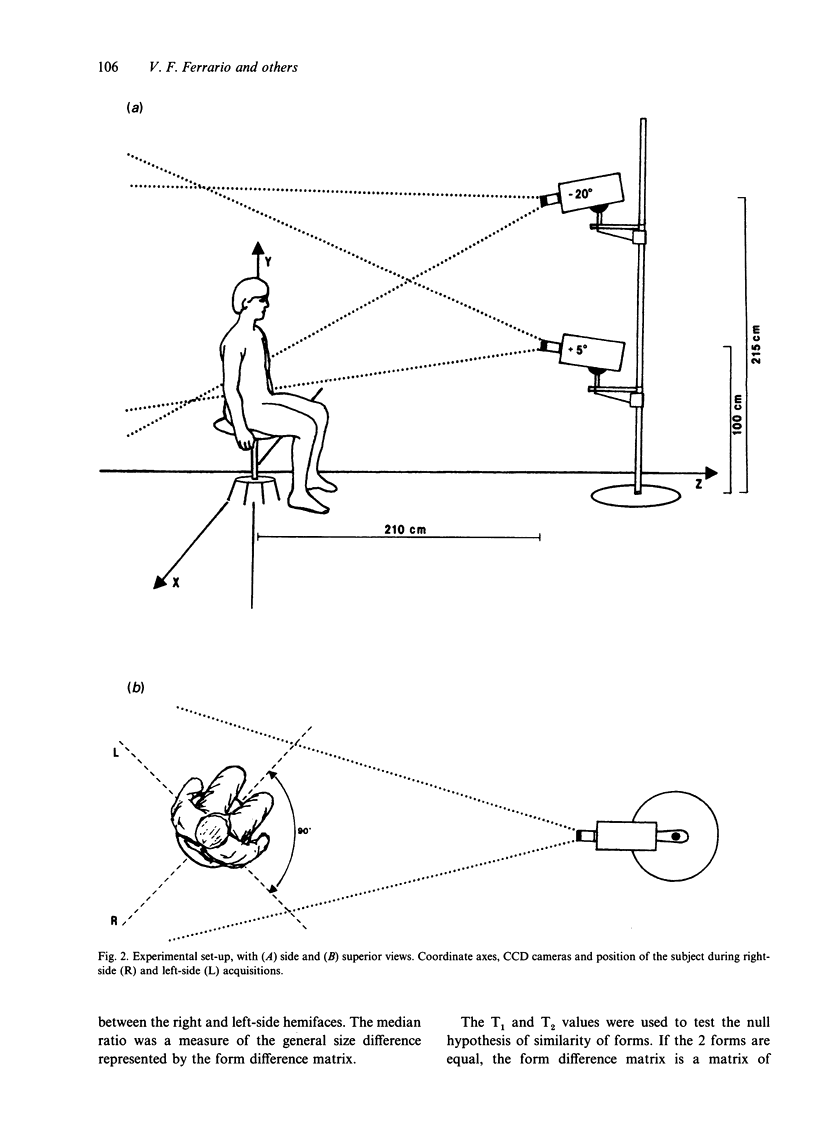
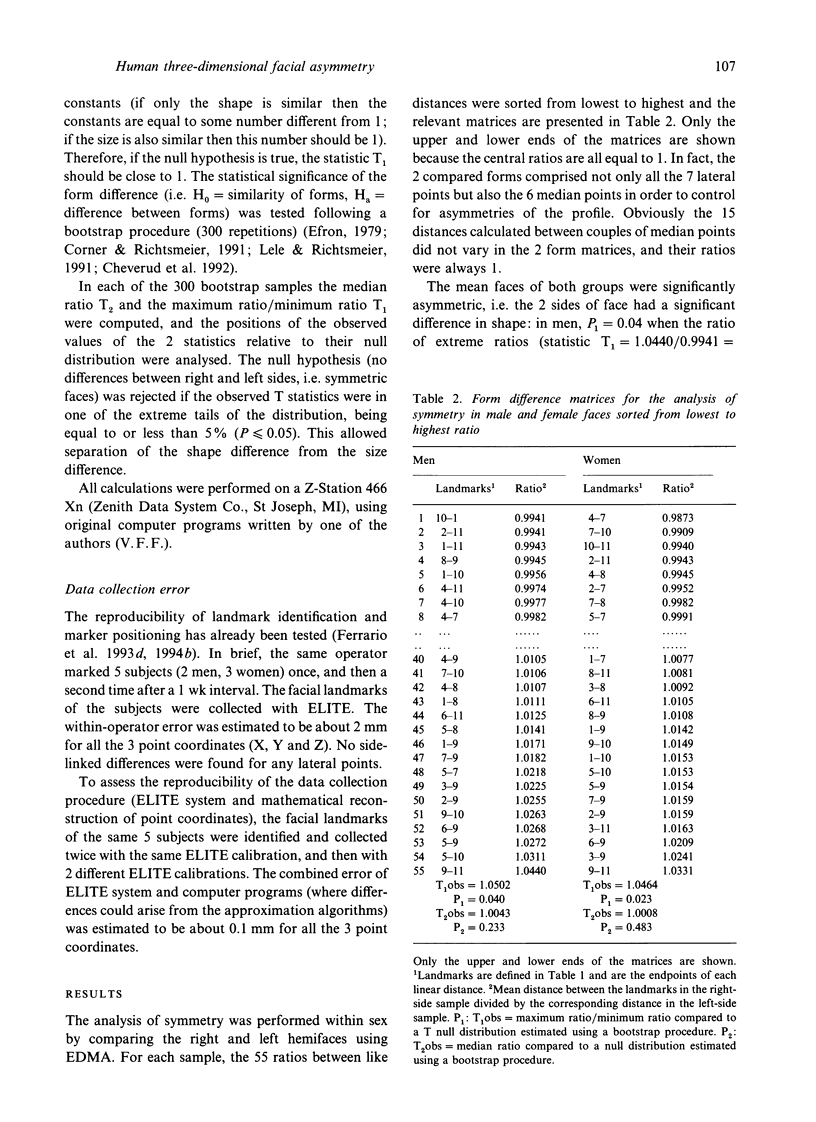
Soft-tissue facial asymmetry was studied in a group of 80 young healthy white Caucasian adults (40 men, 40 women) with no craniofacial, dental or mandibular disorders. For each subject, the 3-dimensional coordinates of 16 standardised soft-tissue facial landmarks (trichion, nasion, pronasale, subnasale, B point, pogonion, eye lateral canthi, nasal alae, labial commissures, tragi, gonia) were measured by infrared photogrammetry by an automated instrument. The form of the right and left hemifaces was assessed by calculating all the possible linear distances between pairs of landmarks within side. Side differences were tested by using euclidean distance matrix analysis. The mean faces of both groups were significantly asymmetric, i.e. the 2 sides of face showed significant differences in shape, but no differences in size.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alavi D. G., BeGole E. A., Schneider B. J. Facial and dental arch asymmetries in Class II subdivision malocclusion. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1988 Jan;93(1):38–46. doi: 10.1016/0889-5406(88)90191-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bookstein F. L. A statistical method for biological shape comparisons. J Theor Biol. 1984 Apr 7;107(3):475–520. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(84)80104-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheverud J. M., Kohn L. A., Konigsberg L. W., Leigh S. R. Effects of fronto-occipital artificial cranial vault modification on the cranial base and face. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1992 Jul;88(3):323–345. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.1330880307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corner B. D., Richtsmeier J. T. Morphometric analysis of craniofacial growth in Cebus apella. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1991 Mar;84(3):323–342. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.1330840308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Mangoury N. H., Shaheen S. I., Mostafa Y. A. Landmark identification in computerized posteroanterior cephalometrics. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1987 Jan;91(1):57–61. doi: 10.1016/0889-5406(87)90209-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrario V. F., Sforza C., Colombo A., Miani A., Jr, D'Addona A. Position and asymmetry of teeth in untreated dental arches. Int J Adult Orthodon Orthognath Surg. 1993;8(4):277–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrario V. F., Sforza C., D'Addona A., Miani A., Jr, Poggio C. E. ANB skeletal types correlated to facial morphology: Euclidean distance matrix analysis. Int J Adult Orthodon Orthognath Surg. 1993;8(3):181–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrario V. F., Sforza C., Miani A., Jr, Tartaglia G. Human dental arch shape evaluated by euclidean-distance matrix analysis. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1993 Apr;90(4):445–453. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.1330900405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrario V. F., Sforza C., Miani A., Jr, Tartaglia G. Maxillary versus mandibular arch form differences in human permanent dentition assessed by Euclidean-distance matrix analysis. Arch Oral Biol. 1994 Feb;39(2):135–139. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(94)90108-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrario V. F., Sforza C., Pizzini G., Vogel G., Miani A. Sexual dimorphism in the human face assessed by euclidean distance matrix analysis. J Anat. 1993 Dec;183(Pt 3):593–600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrigno G., Pedotti A. ELITE: a digital dedicated hardware system for movement analysis via real-time TV signal processing. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 1985 Nov;32(11):943–950. doi: 10.1109/TBME.1985.325627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LU K. H. HARMONIC ANALYSIS OF THE HUMAN FACE. Biometrics. 1965 Jun;21:491–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lele S., Richtsmeier J. T. Euclidean distance matrix analysis: a coordinate-free approach for comparing biological shapes using landmark data. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1991 Nov;86(3):415–427. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.1330860307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lele S., Richtsmeier J. T. On comparing biological shapes: detection of influential landmarks. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1992 Jan;87(1):49–65. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.1330870106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lele S. Some comments on coordinate-free and scale-invariant methods in morphometrics. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1991 Aug;85(4):407–417. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.1330850405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melnik A. K. A cephalometric study of mandibular asymmetry in a longitudinally followed sample of growing children. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1992 Apr;101(4):355–366. doi: 10.1016/S0889-5406(05)80329-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck S., Peck L., Kataja M. Skeletal asymmetry in esthetically pleasing faces. Angle Orthod. 1991 Spring;61(1):43–48. doi: 10.1043/0003-3219(1991)061<0043:SAIEPF>2.0.CO;2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirttiniemi P., Kantomaa T., Lahtela P. Relationship between craniofacial and condyle path asymmetry in unilateral cross-bite patients. Eur J Orthod. 1990 Nov;12(4):408–413. doi: 10.1093/ejo/12.4.408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid W., Mongini F., Felisio A. A computer-based assessment of structural and displacement asymmetries of the mandible. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1991 Jul;100(1):19–34. doi: 10.1016/0889-5406(91)70045-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah S. M., Joshi M. R. An assessment of asymmetry in the normal craniofacial complex. Angle Orthod. 1978 Apr;48(2):141–148. doi: 10.1043/0003-3219(1978)048<0141:AAOAIT>2.0.CO;2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tng T. T., Chan T. C., Cooke M. S., Hägg U. Effect of head posture on cephalometric sagittal angular measures. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1993 Oct;104(4):337–341. doi: 10.1016/S0889-5406(05)81330-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vig P. S., Hewitt A. B. Asymmetry of the human facial skeleton. Angle Orthod. 1975 Apr;45(2):125–129. doi: 10.1043/0003-3219(1975)045<0125:AOTHFS>2.0.CO;2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson E. H., Simmons M. D. Mandibular asymmetry and its relation to pain dysfunction. Am J Orthod. 1979 Dec;76(6):612–617. doi: 10.1016/0002-9416(79)90207-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


