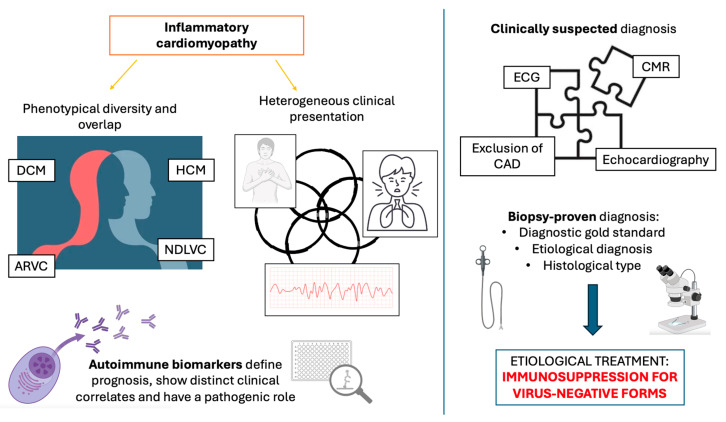
Figure 1.
Overview of a guideline-based clinical and diagnostic approach to inflammatory cardiomyopathy. Inflammatory cardiomyopathy presents a high grade of clinical heterogeneity (clinical presentation may range from chronic heart failure to abrupt onset of life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias) and phenotypical diversity (non-invasive findings may mimic other cardiomyopathies such as ARVC, DCM, etc.). Autoimmune biomarkers may suggest an immune-mediated etiology and identify patients with worse phenotype and follow-up [35,36]. A diagnosis of clinically suspected myocarditis is mostly based on CMR findings, but only EMB can achieve a definitive and etiological diagnosis, possibly identifying candidates for tailored immunosuppression in virus-negative cases. ARVC: left ventricular cardiomyopathy; CAD: coronary artery disease; DCM: dilated cardiomyopathy; ECG: electrocardiogram; HCM: hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Created with Biorender.