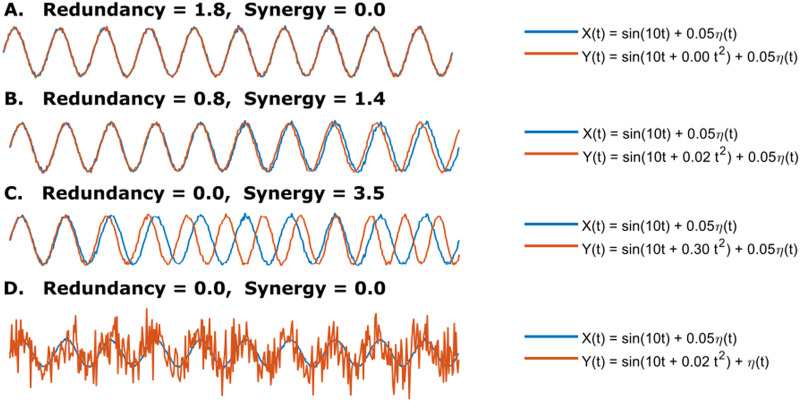
Figure 1. .
Given two random variables X(t) = sin(10t) + 0.05η(t) and Y(t) = sin(10t + it2) + 0.05η(t), with i = {0, 0.02, 0.3}, t ∈ [0, 2π], and η ∼ 𝒩(0, 1). (A) Full redundancy and zero synergy. (B) The redundancy decreases when i = 0.02. (C) Full synergy and zero redundancy when i = 0.3. (D) Synergy and redundancy are zero when Y(t) = sin(10t + 0.02t2) + η(t).