Fig. 4. Comparing prevalence of post-COVID-19 symptoms by BMI intraindividual variability (CV) quartile subgroups, and sensitivity analysis via causal mediation modeling.
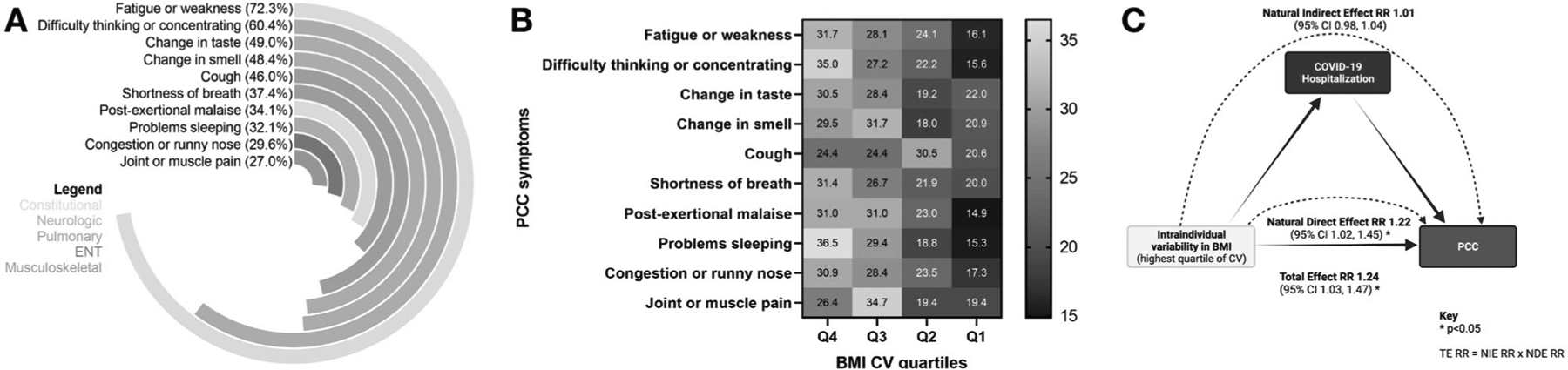
A Among participants with PCC during the study, percentages of the top 10 specific symptoms of PCC are illustrated. B For each PCC symptom, we compared of the proportion of donors across BMI CV quartiles. Among donors with fatigue or weakness, difficulty thinking or concentrating, and problems sleeping, higher proportions had elevated BMI variability (all three p < 0.05). C To confirm findings of the association between PCC and BMI variability (CV), we considered COVID-19 hospitalization as a potential mediator. The causal mediation model framework figure was created with BioRender.com. BMI body mass index, CV coefficient of variation, PCC post-COVID conditions.
