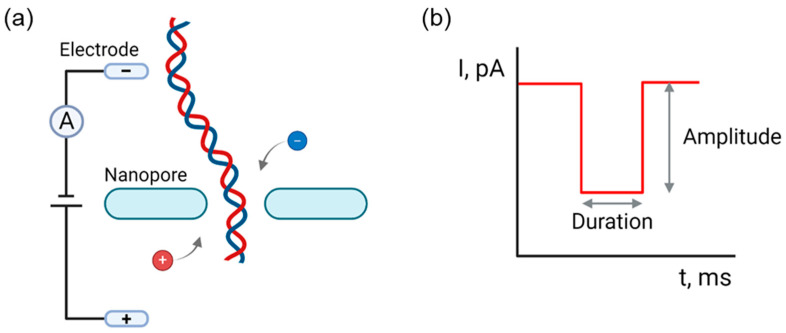
Figure 1.
Nanopore detection. (a) Experimental principle of nanopore detection. Two baths filled with an electrolyte solution, typically a buffered salt solution, are separated by a single nanopore (or nanopipette). Ag/AgCl electrodes are immersed in the bath and a constant voltage bias is applied across the nanopore. When a molecule translocates through the nanopore, the ionic current typically decreases. (b) Characteristics of translocation event. The amplitude and duration (dwell time) of the current reduction during translocation can provide critical insights about biomolecules. Created with Biorender.com.