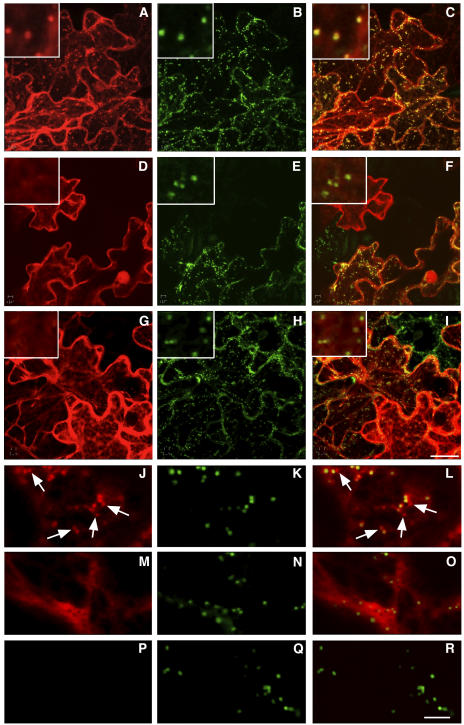
Figure 7.
RAB-E1d Targets YFP to the Golgi via a GTP- and Prenylation-Dependent Mechanism.
(A) to (C) Confocal analysis of cells coexpressing YFP-RAB-E1d (A) and ST-GFP (B). (C) is merged from the YFP-RAB-E1d image (A) and the ST-GFP image (B). Note the precise colocalization of YFP-RAB-E1d–labeled punctate structures and Golgi (insets).
(D) to (F) Confocal analysis of tobacco epidermal cells coexpressing YFP-RAB-E1d[SN] (D) and ST-GFP (E). (F) was obtained by merging images (D) and (E). Note the exclusively cytosolic YFP-RAB-E1d[SN] fluorescence in (D).
(A) to (I) are projections on the z axis of a series of optical sections of the cortical cytoplasm. Bar in (I) = 25 μm for (A) to (I).
(G) to (I) Confocal analysis of tobacco epidermal cells coexpressing YFP-RAB-E1dΔCC (G) and ST-GFP (H). (I) was obtained by merging (G) and (H). Like YFP-RAB-E1d[SN], YFP-RAB-E1dΔCC fluorescence is exclusively cytosolic (G). Insets in (D) to (I) show regions of each image at higher resolution, confirming that YFP-tagged RAB-E1d mutants do not colocalize with Golgi stacks.
(J) to (L) Confocal analysis of a tobacco epidermal cell coexpressing YFP-RAB-D2a (J) and ST-GFP (K). (L) was obtained by merging (J) and (K). Arrows identify examples of YFP-RAB-D2a–labeled punctate structures that are distinct from the Golgi stacks.
(M) to (O) Confocal analysis of a tobacco epidermal cell coexpressing YFP-RAB-D2a[SN] (M) and ST-GFP (N). (O) was obtained by merging (M) and (N). Note the exclusive cytosolic YFP-RAB-D2a[SN] fluorescence in (M).
(P) to (R) Confocal images of a control tobacco epidermal cell expressing ST-GFP. The images were captured with identical confocal laser scanning parameters used for (J) to (O). (R) is merged from (P) and the ST-GFP image (Q). The absence of signal in the YFP image (P) excludes the possibility that the Golgi-sized faint punctate structures in (J) represented bleed-through of GFP fluorescence into the YFP detection channel. Bar in (R) = 5 μm for (J) to (R).