Abstract
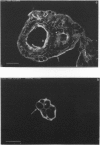
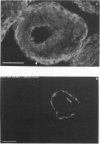
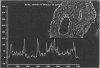
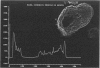
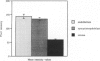
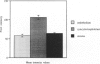
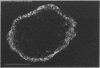
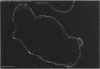
The human IgG subclasses are a family of highly related yet distinct molecules. Each of these four subclasses performs a discrete function within the human immune system. Previous studies have shown that one of these molecules, hIgG2, may be discriminated against in transport across the human placenta. We have aimed to elucidate the mechanism of this discrimination in order to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the process of transport of immunoglobulin across the human placenta. We have used a combination of immunocyctochemical localisation and biochemical analysis to detail the behaviour of hIgG2. Confocal laser scanning microscopy was used to compare the localisation of hIgG1 (chosen as representative of the efficiently transported subclasses) and hIgG2 in term and first trimester chorionic villi. Complementary evidence was provided from immunoblot analysis of isolated placental coated vesicles. The data presented here suggest that the hIgG2 is transported into the syncytiotrophoblast and appears to accumulate in the stroma of the villi. This leads us to the hypothesis that the fetal capillary endothelium is the cellular impediment to the transport of hIgG2 into the fetal circulation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- FRANKLIN E. C., KUNKEL H. G. Comparative levels of high molecular weight (19S) gamma globulin in maternal and umbilical cord sera. J Lab Clin Med. 1958 Nov;52(5):724–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frangione B., Franklin E. C., Fudenberg H. H., Koshland M. E. Structural studies of human gamma-G-myeloma proteins of different antigenic subgroups and genetic specificities. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):715–732. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREY H. M., KUNKEL H. G. H CHAIN SUBGROUPS OF MYELOMA PROTEINS AND NORMAL 7S GAMMA-GLOBULIN. J Exp Med. 1964 Aug 1;120:253–266. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.2.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUBB R., LAURELL A. B. Hereditary serological human serum groups. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1956;39(6):390–398. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1956.tb05067.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitlin D., Biasucci A. Development of gamma G, gamma A, gamma M, beta IC-beta IA, C 1 esterase inhibitor, ceruloplasmin, transferrin, hemopexin, haptoglobin, fibrinogen, plasminogen, alpha 1-antitrypsin, orosomucoid, beta-lipoprotein, alpha 2-macroglobulin, and prealbumin in the human conceptus. J Clin Invest. 1969 Aug;48(8):1433–1446. doi: 10.1172/JCI106109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Anderson R. G., Brown M. S. Coated pits, coated vesicles, and receptor-mediated endocytosis. Nature. 1979 Jun 21;279(5715):679–685. doi: 10.1038/279679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy H. O., Peltz G., Moore K. W., Golbus M. S., Jackson L. G., Lebo R. V. The polymorphic Fc gamma receptor II gene maps to human chromosome 1q. Immunogenetics. 1989;29(5):331–339. doi: 10.1007/BF00352843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. G. Human IgG subclass measurements in the clinical laboratory. Clin Chem. 1987 Oct;33(10):1707–1725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler P. F., Farr R. S. Elevation of cord over maternal IgG immunoglobulin: evidence for an active placental IgG transport. Nature. 1966 Jun 4;210(5040):1070–1071. doi: 10.1038/2101070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINNET-JEPSEN P., GALATIUS-JENSEN F., HAUGE M. On the inheritance of the Gm serum group. Acta Genet Stat Med. 1958;8(2):164–196. doi: 10.1159/000151065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell A., Skvaril F., van Loghem E., Kleemola M. Human IgG subclasses in maternal and fetal serum. Vox Sang. 1971 Dec;21(6):481–492. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1971.tb04808.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell A., Terry W. D., Waldmann T. A. Metabolic properties of IgG subclasses in man. J Clin Invest. 1970 Apr;49(4):673–680. doi: 10.1172/JCI106279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natvig J. B., Kunkel H. G. Human immunoglobulins: classes, subclasses, genetic variants, and idiotypes. Adv Immunol. 1973;16:1–59. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60295-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockleford C. D., Clint J. M. The uptake of IgG by human placental chorionic villi: a correlated autoradiographic and wide aperture counting study. Placenta. 1980 Apr-Jun;1(2):91–111. doi: 10.1016/s0143-4004(80)80018-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse B. M. Coated vesicles from human placenta carry ferritin, transferrin, and immunoglobulin G. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):451–455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitcher-Wilmott R. W., Hindocha P., Wood C. B. The placental transfer of IgG subclasses in human pregnancy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Aug;41(2):303–308. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiu W. Q., de Bruin D., Brownstein B. H., Pearse R., Ravetch J. V. Organization of the human and mouse low-affinity Fc gamma R genes: duplication and recombination. Science. 1990 May 11;248(4956):732–735. doi: 10.1126/science.2139735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. C., Faulk W. P., Stuckey M. A., Fudenberg H. H. Chemical differences of adult, fetal and hypogammaglobulinemic IgG immunoglobulins. Immunochemistry. 1970 Aug;7(8):703–708. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90176-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warmerdam P. A., van de Winkel J. G., Gosselin E. J., Capel P. J. Molecular basis for a polymorphism of human Fc gamma receptor II (CD32). J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):19–25. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warmerdam P. A., van de Winkel J. G., Vlug A., Westerdaal N. A., Capel P. J. A single amino acid in the second Ig-like domain of the human Fc gamma receptor II is critical for human IgG2 binding. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 15;147(4):1338–1343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Winkel J. G., Anderson C. L. Biology of human immunoglobulin G Fc receptors. J Leukoc Biol. 1991 May;49(5):511–524. doi: 10.1002/jlb.49.5.511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]