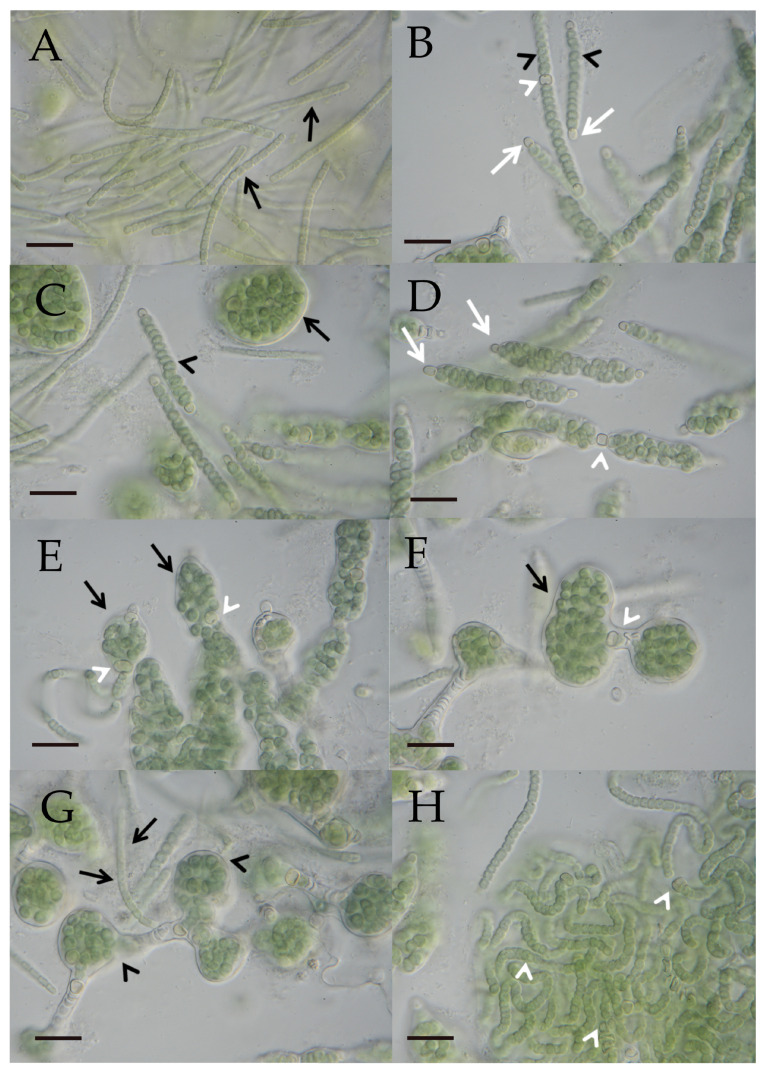
Figure 4.
(A–H) Photographic documentation of the “Nostoc”-type morphotype (L066/CCAC 7008B/BEA 1768B) in a developmental sequence. (A) Several hormogonia (black arrows) characterized by barrel-shaped cells. Scale bar = 10 µm. (B) Differentiated filaments show lenticular to sublenticular vegetative cells (black arrowheads). Spherical to subspherical terminal heterocytes (white arrows) first appear on both ends of a filament, followed by a lenticular to sublenticular intercalary heterocyte (white arrowhead). Scale bar = 10 µm. (C) A common sheath develops surrounding the filament (black arrowhead). Within the sheath, vegetative cells continue to divide, expanding the sheath, with the filament eventually forming a globular structure (black arrow). Scale bar = 10 µm. (D) Terminal heterocytes (white arrows) and the initial intercalary heterocyte (white arrowhead) lack a sheath. Scale bar = 10 µm. (E,F) Curled filaments within expanded sheaths (black arrows) held together by intercalary heterocytes (white arrowheads). Scale bars = 10 µm. (G) When the flexible sheath (black arrowheads) breaks open, hormogonia (black arrows) emerge from the globular structures and start the developmental cycle again. Scale bar = 10 µm. (H) Filaments with intercalary heterocytes (white arrowheads) derived from a broken globular structure. Scale bar = 10 µm.