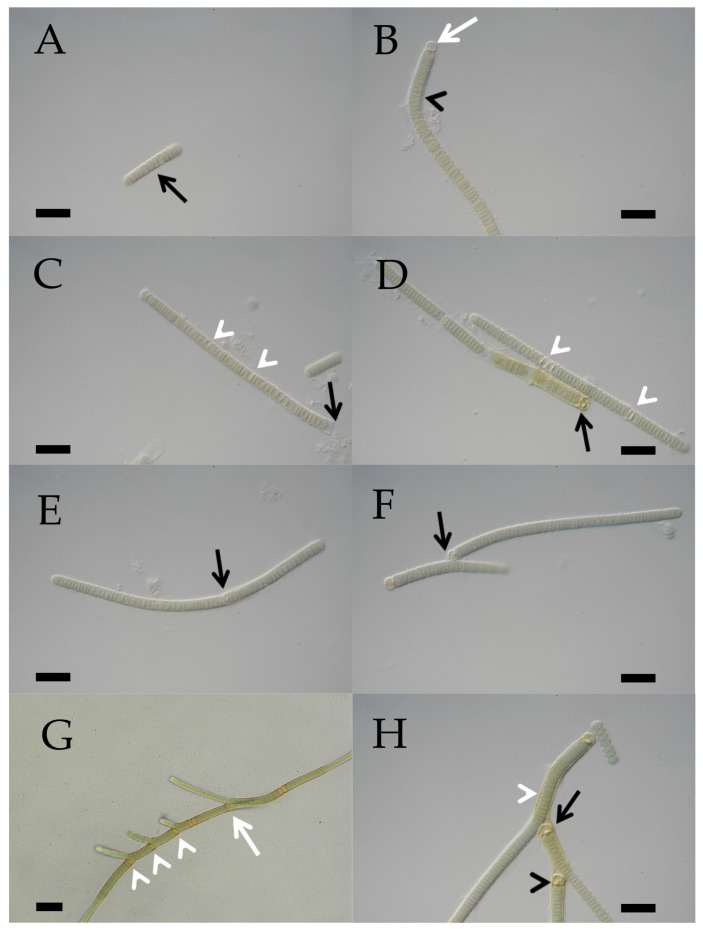
Figure 5.
(A–H) Photographic documentation of the “Tolypothrix”-type morphotype (L088/CCAC 7034B/BEA 1790B) in a developmental sequence. (A) Hormogonia are characterized by lenticular to sublenticular cells (black arrow): note the slight polarity of the filament. Scale bar = 10 µm. (B) An older filament with lenticular to sublenticular vegetative cells (black arrowhead) and a spherical to subspherical terminal heterocyte (white arrow). Scale bar = 10 µm. (C) A firm sheath (black arrow) surrounds the straight filament. Early developmental stages of differentiation of intercalary heterocytes from vegetative cells (white arrowheads). Scale bar = 10 µm. (D) Lenticular to sublenticular differentiated intercalary heterocytes (white arrowheads; the left arrowhead depicts two adjacent intercalary heterocytes). The intercalary heterocytes remain enclosed in the firm sheath (unlike the situation in the “Nostoc”-type morphotype). A yellowish firm sheath surrounds vegetative cells of an older filament near a terminal heterocyte (black arrow). Scale bar = 10 µm. (E) Very early stage of the formation of a false branch. A vegetative cell adjacent to an intercalary heterocyte dissociates from the heterocyte and starts to bulge the sheath (black arrow). The intercalary heterocyte of the filament thus becomes a new terminal heterocyte. Scale bar = 10 µm. (F) A false branch attached to a heterocyte (black arrow). Scale bar = 10 µm. (G) Several false branches arising from vegetative cells adjacent to intercalary heterocytes (white arrowheads) or a necrotic cell (white arrow). Scale bar = 20 µm. (H) A primary (black arrow) and a secondary (black arrowhead) false branch share the same firm sheath (white arrowhead). Scale bar = 10 µm.