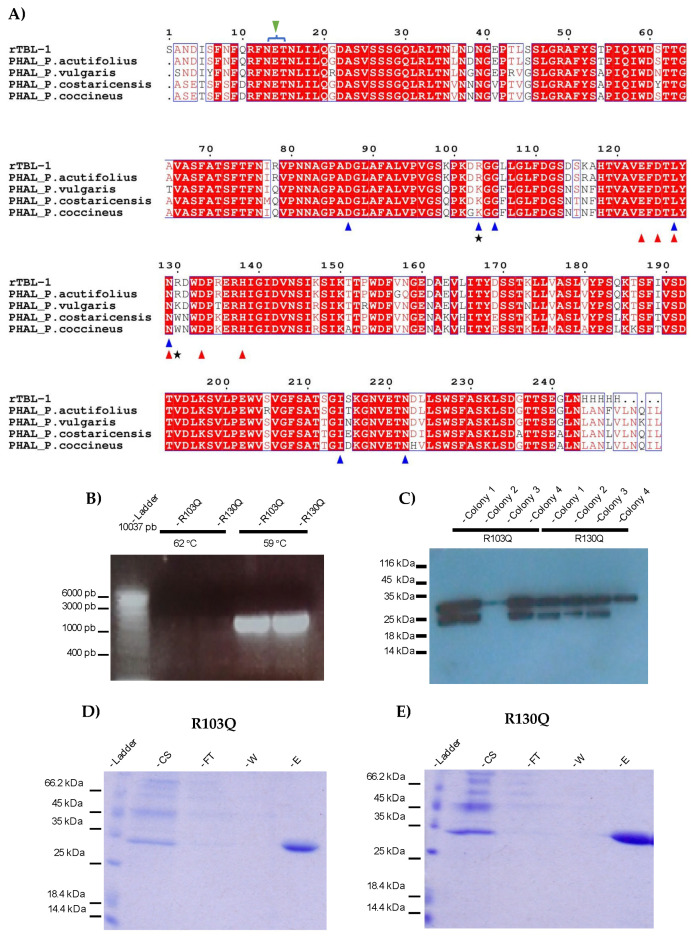
Figure 1.
Mutants’ design and production. (A) Sequence alignment of rTBL-1 homologous lectins. PHAL_Phaseolus costaricensis (Q5ZF34_9FABA), PHAL_Phaseolus coccineus (Q84RP8_PHACN), PHAL_Phaseolus vulgaris (PHAL_PHAVU), PHAL_Phaseolus acutifolius (Q40750_PHAAT), rTBL-1 sequence [14]. White letters represent identical residues, semiconserved residues are displayed in red enclosed into empty boxes and non-conserved residues are depicted in black. Blue triangles show residues that correspond to the CBP similarly to PHA-L from P. Vulgaris; red triangles show residues interacting with metal cations; green triangle depicts sequence for N-glycosylation marked with a blue bracket; black stars show residues presumably responsible for the cytotoxic effect of rTBL-1 (R103 and R130). (B) Agarose gel electrophoresis showing pGAPαZB-rTBL-1 vector amplification. Lane 1, ladder; lanes 2–5, amplification products. (C) Western blot screening using anti-His antibodies for transformed colonies. (D,E) R103Q and R130Q SDS-PAGE electrophoretic profiles stained for total protein. Lane 1, ladder; lane 2, 25 µL of culture supernatant (CS); lane 3, 25 µL of flow through (FT); lane 4, 25 µL wash with 10 mM imidazole buffer (W); and lane 5, 25 µL elution with 200 mM imidazole buffer (E). PHAL, Leukocyte phytohemagglutinin.