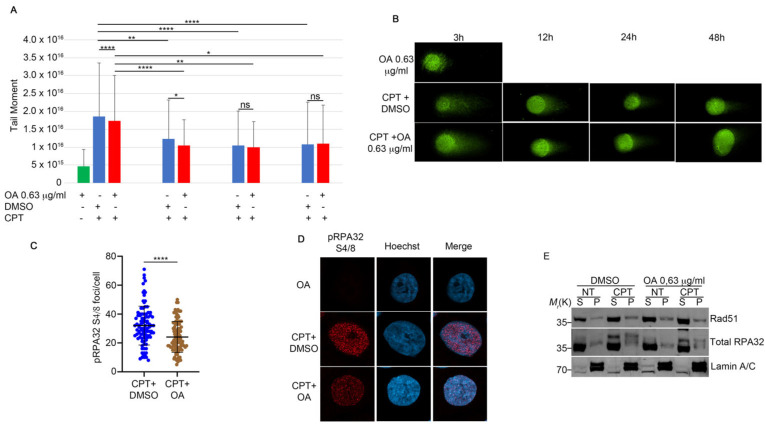
Figure 4.
OA treatment does not affect the DNA repair ability compared to CPT alone. (A) The neutral comet assay was performed as described in Section 4. HeLa cells were pre-treated with OA or DMSO, followed by incubation with 1 μM CPT for an additional two hours. At the end of the incubation period, a drug washout was performed to monitor DNA repair. For each condition, 5 × 10⁴ cells were spotted onto glass slides and stained with SYBR Green. We analyzed 30 cells for each condition. The results show the means and standard deviation (SD) of three independent experiments. Statistically significant differences are indicated by * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and **** p < 0.0001. (B) Representative images of the neutral comet assay. Magnification 63×. (C) Immunofluorescence analysis of pRPA32 S4/8 foci per cell in HeLa cells treated with CPT alone or in combination with OA. Immunofluorescence staining was performed with pRPA32 S4/8, and Hoechst was used as a DNA marker. We analyzed 30 cells for each condition across three independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed using a t-test, and significant differences are indicated by **** p < 0.0001. (D) Representative images of pRPA32 S4/8 in HeLa cells treated as described in (C). Magnification 63×. (E) HeLa cells were pre-treated with 0.63 µg/mL of OA for one hour, followed by incubation with 1 µM CPT for an additional two hours. Chromatin-enriched purification was performed to separate soluble (S) and chromatin-bound (P) fractions. RPA32 protein was used as a marker for the soluble fraction and as a control for DNA damage, while Lamin A/C served as a loading control for the chromatin fraction.