Figure 4. Ac-α-syn binding on lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) shows high intermolecular interactions.
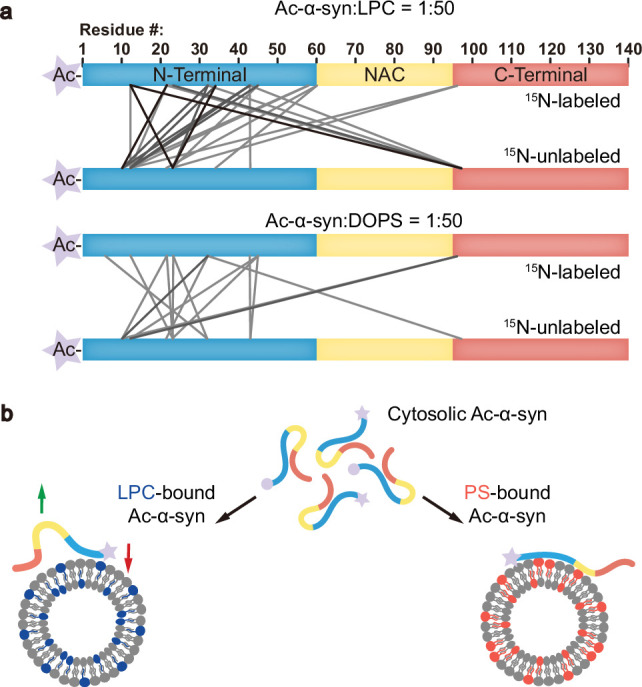
(a) The cross-linking patterns of Ac-α-syn in the presence of LPC and dioleoyl-phosphoserine (DOPS) mapped by mass spectrometry (MS) at the protein/lipid molar ratio of 1:50. Lines present the inter-molecular cross-linked residues between two individual 15N-labeled and unlabeled Ac-α-syn. The grayscale of the lines corresponds to the frequency of the cross-linked pairs identified in three individual experiments. Source data are provided in Supplementary file 1a-f. (b) Ac-α-syn binds strongly to LPC through the N-terminal region (red arrow), and leaves more unbound NAC and C-terminal region for intermolecular interaction (green arrow). In contrast, N-terminal acetylation reduces α-syn’s binding to DOPS, and due to the negatively charged headgroup of PS, Ac-α-syn binding on DOPS extends to the NAC region, which limits intermolecular interactions. Supplementary file 1 (a-–c) Three biological replicates of identified cross-linked peptides between 15N-Ac-α-syn and 14N-Ac-α-syn in LPC; (d-e) Three biological replicates of identified cross-linked peptides between 15N-Ac-α-syn and 14N-Ac-α-syn in DOPS; Protein:lipid = 1:50, mol:mol.
