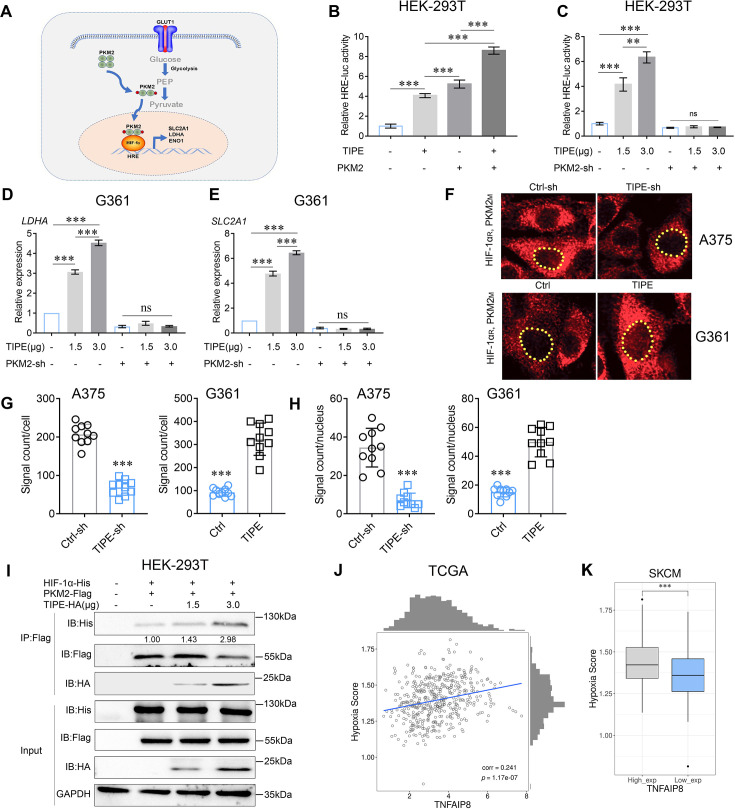
Figure 3. TIPE promotes HIF-1α transcription in a PKM2-dependent manner.
(A) Proposed molecular mechanism by which dimeric PKM2 regulates cell proliferation and glycolysis by modulating HIF-1α activity. (B) TIPE, especially when combined with PKM2, boosts relative hypoxia response element (HRE) luciferase activity, as examined by luciferase reporter assay. (C) TIPE promoted HRE activity in a dose- and PKM2-dependent manner. (D, E) TIPE increases HIF-1α targeted genes, including LDHA and SLC2A1, in a dose- and PKM2-dependent manner. (F, G) TIPE promoted endogenous interaction between PKM2 and HIF-1α in melanoma cells using a Doulink assay. Interference of TIPE in A375 cells promoted the interaction between PKM2 and HIF-1α (upper) compared to that overexpression of TIPE in G361 cells decreased their interaction (lower). The density of the red color signaling means the interactive strength between PKM2 and HIF-1α affected by TIPE. (H) TIPE enhanced the PKM2/HIF1a interaction in the nucleus. (I) TIPE increased the exogenous interaction between PKM2 and HIF-1α in a dose- dependent manner in HEK-293T cells. (J) TCGA dataset revealed that TIPE has a positive relationship with hypoxia score in melanoma. (K) Higher expression of TIPE is associated with a relatively higher hypoxia score in melanoma. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. The data represent the means ± SEM of three replicates *p<0.05.