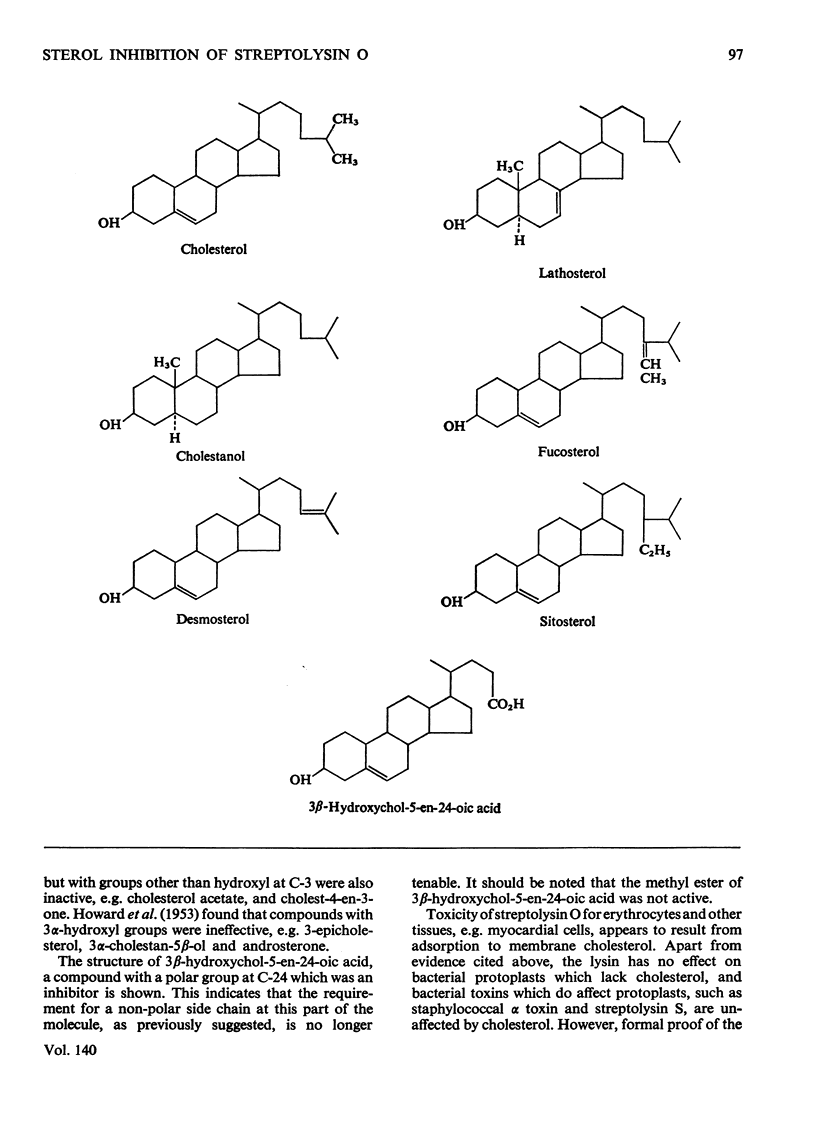
Abstract
Reduced streptolysin O, a toxin produced by certain β-haemolytic streptococci, lyses human erythrocytes. The reaction is inhibited by cholesterol at concentrations of about 1.0μg/ml. Other sterols inhibit the lysin and there is a specific requirement for a 3β-hydroxyl group. Inhibition was obtained with 3β-hydroxychol-5-en-24-oic acid, containing a hydrophilic group at C-24. The mode of inhibition is likely to involve attachment to the fixation site of the lysin which attaches the molecule to cell membranes, probably to membrane cholesterol. A second streptolysin site, concerned in the final haemolytic event, may also be involved. Inhibitors of the latter site have not been characterized, other than antibody with specificity for the site.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernheimer A. W. Disruption of wall-less bacteria by streptococcal and staphylococcal toxins. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):1677–1680. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.1677-1680.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWARD J. G., WALLACE K. R., WRIGHT G. P. The inhibitory effects of cholesterol and related sterols on haemolysis by streptolysin O. Br J Exp Pathol. 1953 Apr;34(2):174–180. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen K. F., Nowak P., Thiele O. W., Urbaschek B. Investigations concerning the action of streptolysin O and its unspecific inhibition by lipids. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(1):69–81. doi: 10.1159/000229688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson K. C., Rose T. P., Kerr E. J. Some factors influencing the effect of cholesterol on streptolysin O activity. J Clin Pathol. 1972 Oct;25(10):885–891. doi: 10.1136/jcp.25.10.885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


