Abstract
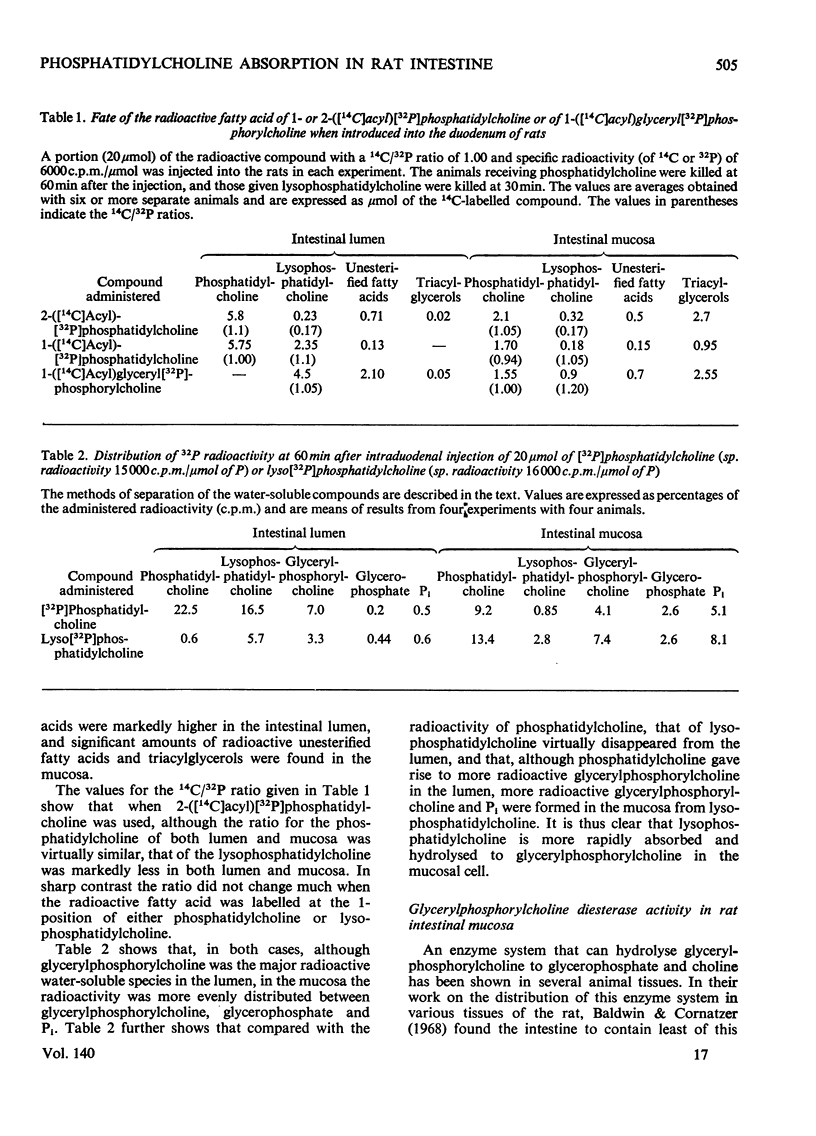
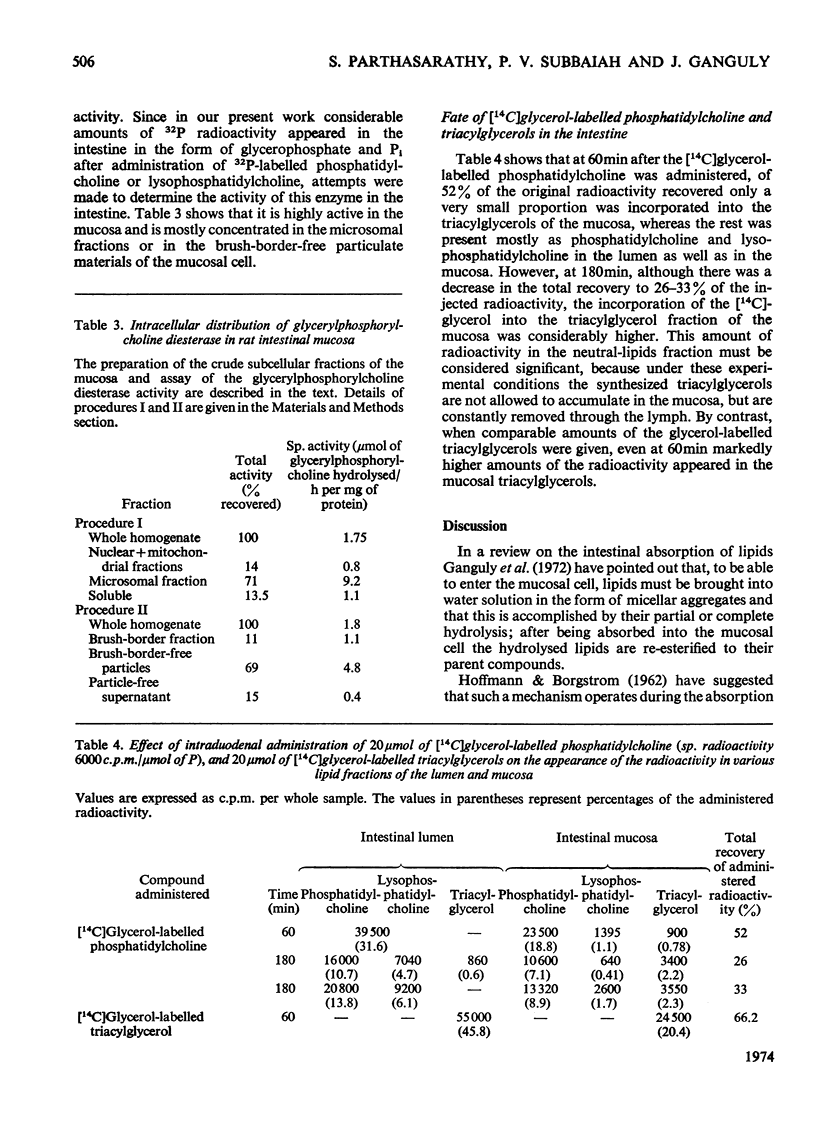
1. The mechanism of absorption of phosphatidylcholine was studied in rats by injecting into the intestine phosphatidylcholine specifically labelled either in the fatty acid or in the glycerol moiety or with 32P, when considerable amounts of 1-acyl-lysophosphatidylcholine were found in the intestinal lumen. 2-([14C]Acyl)phosphatidylcholine gave markedly more radioactive unesterified fatty acids in the lumen, compared with the 1-([14C]acyl) derivative. Some of the radioactivity from either the fatty acid or the glycerol moiety of the injected phosphatidylcholine appeared in the mucosal triacylglycerols. 2. Injection of 32P-labelled phosphatidylcholine or 32P-labelled lysophosphatidylcholine led to the appearance of radioactive glycerylphosphorylcholine, glycerophosphate and Pi in the mucosa. 3. Rat mucosa was found to contain a highly active glycerylphosphorylcholine diesterase. 4. It was concluded that the dietary phosphatidylcholine is hydrolysed in the intestinal lumen by the pancreatic phospholipase A to 1-acylglycerylphosphorylcholine, which on entering the mucosal cell is partly reacylated to phosphatidylcholine, and the rest is further hydrolysed to glycerylphosphorylcholine, glycerophosphate, glycerol and Pi. The fatty acids and glycerophosphate are then reassembled to give triacylglycerols via the Kennedy (1961) pathway.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRAMSON D., BLECHER M. QUANTITATIVE TWO-DIMENSIONAL THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY OF NATURALLY OCCURRING PHOSPHOLIPIDS. J Lipid Res. 1964 Oct;5:628–631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin J. J., Cornatzer W. E. Rat kidney glycerylphosphorylcholine diesterase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Oct 22;164(2):195–204. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(68)90146-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David J. S., Malathi P., Ganguly J. Role of the intestinal brush border in the absorption of cholesterol in rats. Biochem J. 1966 Mar;98(3):662–668. doi: 10.1042/bj0980662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganguly J., Subbaiah P. V., Parthasarathy S. Intestinal absorption of lipids. Biochem Soc Symp. 1972;(35):67–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAESSLER H. A., ISSELBACHER K. J. THE METABOLISM OF GLYCEROL BY INTESTINAL MUCOSA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Jul 9;73:427–436. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90444-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFMANN A. F., BORGSTROM B. Physico-chemical state of lipids in intestinal content during their digestion and absorption. Fed Proc. 1962 Jan-Feb;21:43–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENNEDY E. P. Biosynthesis of complex lipids. Fed Proc. 1961 Dec;20:934–940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd-Davies K. A., Michell R. H., Coleman R. Glycerylphosphorylcholine phosphodiesterase in rat liver. Subcellular distribution and localization in plasma membranes. Biochem J. 1972 Apr;127(2):357–368. doi: 10.1042/bj1270357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER D., CRANE R. K. The digestive function of the epithelium of the small intestine. II. Localization of disaccharide hydrolysis in the isolated brush border portion of intestinal epithelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Sep 16;52:293–298. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90678-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURTHY S. K., DAVID J. S., GANGULY J. SOME OBSERVATIONS ON THE MECHANISM OF ABSORPTION OF CHOLESTEROL IN RATS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Aug 27;70:490–492. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90787-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson A., Borgström B. Absorption and metabolism of lecithin and lysolecithin by intestinal slices. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Apr 4;137(2):240–254. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(67)90100-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson A. Intestinal absorption of lecithin and lysolecithin by lymph fistula rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Mar 4;152(2):379–390. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(68)90047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parthasarathy S., Ganguly J. A simple biosynthetic method for the preparation of glycerol-labelled phosphatidylcholine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 19;296(1):62–64. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90043-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter H. P., Saunders D. R. Isolation of the aqueous phase of human intestinal contents during the digestion of a fatty meal. Gastroenterology. 1971 Jun;60(6):997–1007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTSON A. F., LANDS W. E. Positional specificites in phospholipid hydrolyses. Biochemistry. 1962 Sep;1:804–810. doi: 10.1021/bi00911a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghavan S. S., Ganguly J. Studies on the positional integrity of glyceride fatty acids during digestion and absorption in rats. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(1):81–87. doi: 10.1042/bj1130081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scow R. O., Stein Y., Stein O. Incorporation of dietary lecithin and lysolecithin into lymph chylomicrons in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 10;242(21):4919–4924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subbaiah P. V., Ganguly J. Transesterification of lysolecithin in the intestinal mucosa of rats. Indian J Biochem. 1971 Dec;8(4):197–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subbaiah P. V., Raghavan S. S., Ganguly J. Further studies on the intestinal absorption of triglycerides and fatty acids in rats. Indian J Biochem. 1968 Dec;5(4):147–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


