Figure 1. Risk‐adjusted percentage point changes in outcomes when there is a PCI facility opening within a 15‐minute driving time.
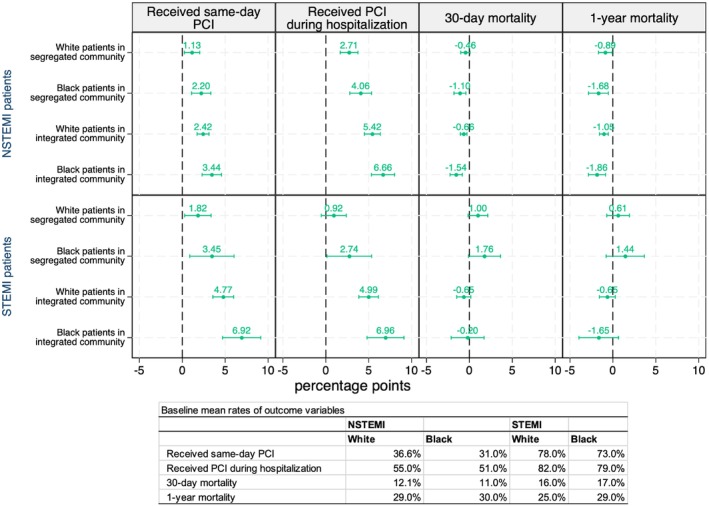
Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals. Community fixed‐effects models are adjusted for patient demographics (5‐year age groups, sex, race) and comorbid conditions (vascular disease, pulmonary disease, diabetes, renal failure, liver disease, cancer, dementia, valvular disease, hypertension, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, arthritis, coagulopathy, obesity, substance abuse, depression, psychosis, hypothyroidism, paralysis and neurological disorder, ulcer, weight loss, fluid and electrolyte disorder, anemia, stroke) and are controlled for yearly trends. Mortality outcomes are also controlled for access and treatment. Reference groups are patients of the same race and community type who did not experience a PCI facility opening. The total population of patients with AMI is 2 388 180 patients (1 861 732 STEMI and 526 448 NSTEMI). The total population of patients with AMI who experienced a PCI facility opening is 379 668 patients (246 096 in integrated and 133 572 in segregated communities). AMI indicates acute myocardial infarction; NSTEMI, non–ST‐segment–elevation myocardial infarction; PCI, percutaneous coronary intervention; and STEMI, ST‐segment–elevation myocardial infarction.
