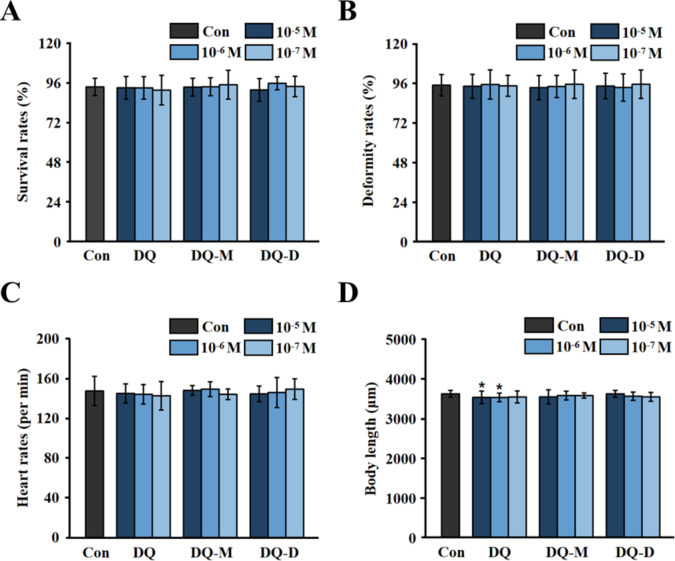
Fig. 2.
DQ, DQ-M, and DQ-D induced developmental toxicity to zebrafish embryos. (A) Survival rates of zebrafish larvae after 96 h exposure to different concentrations of DQ, DQ-M, and DQ-D (N = 60 samples). (B) Deformity rates of zebrafish larvae after 96 h exposure to different concentrations of DQ, DQ-M, and DQ-D (N = 60 samples). (C) Heart rates of zebrafish larvae after 96 h exposure to different concentrations of DQ, DQ-M, and DQ-D (N = 15 samples). (D) Body length of larval zebrafish after 96 h exposure to different concentrations of DQ, DQ-M, and DQ-D (N = 15 samples). Results were shown as mean ± standard deviation (SD) of at least three independent experiments (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001).