Full text
PDF

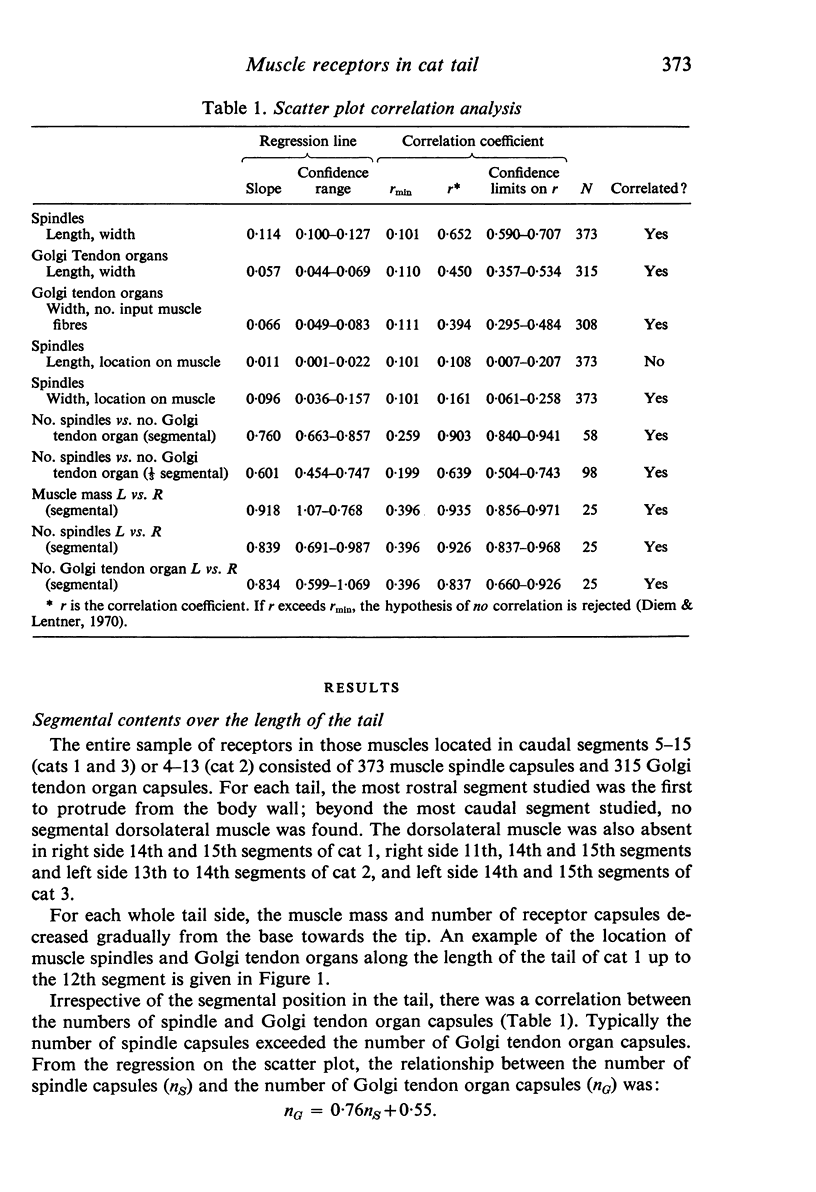
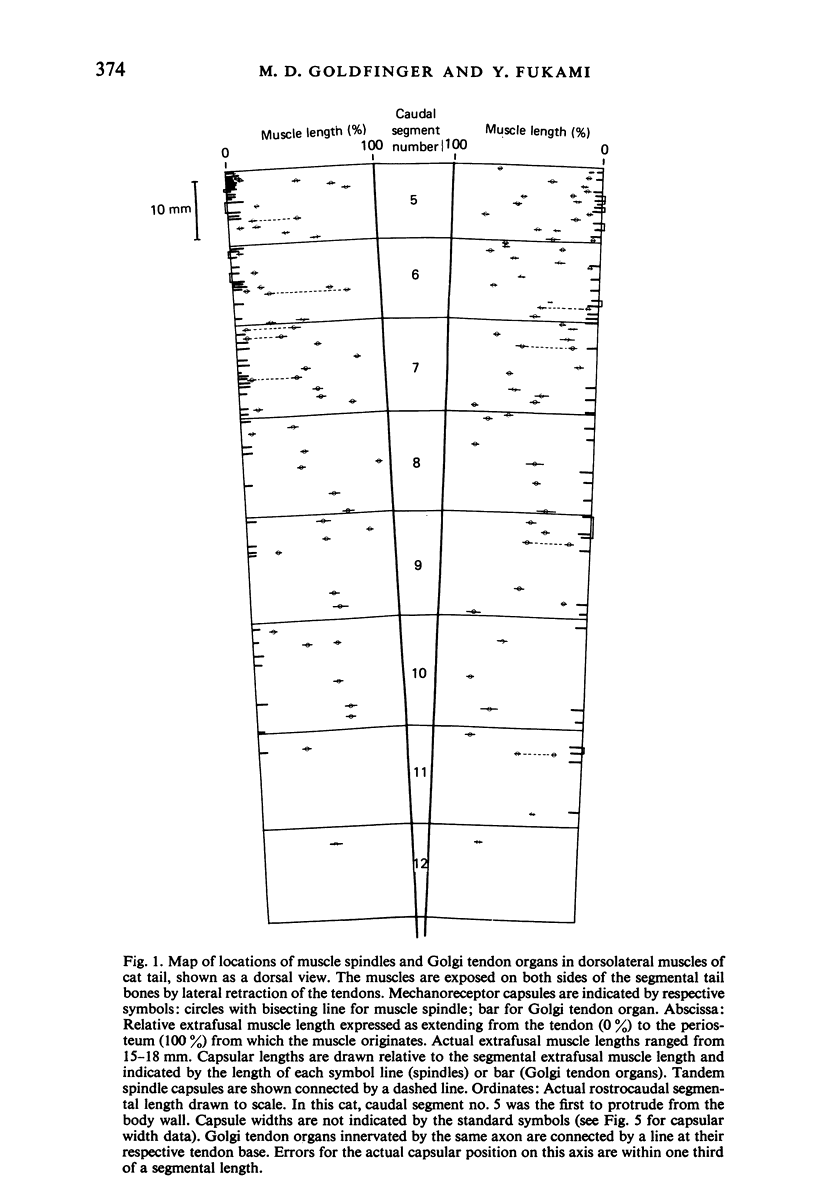
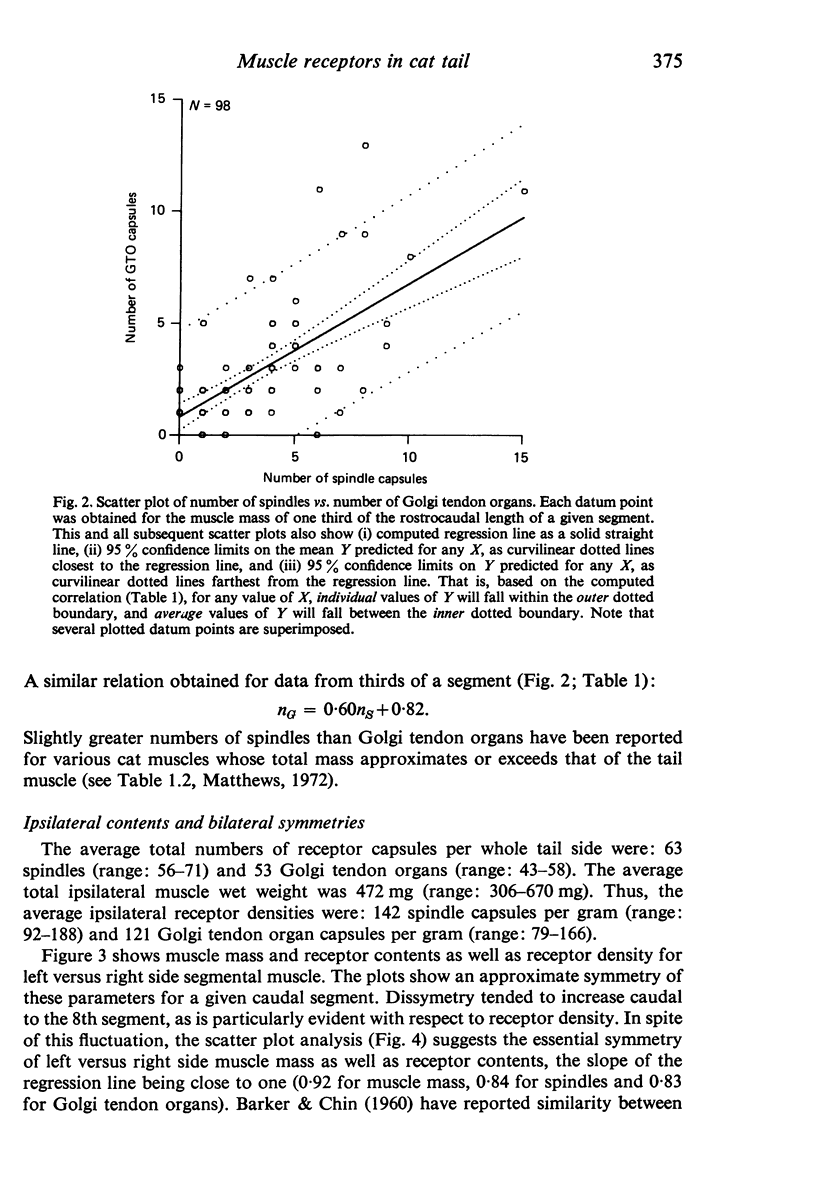
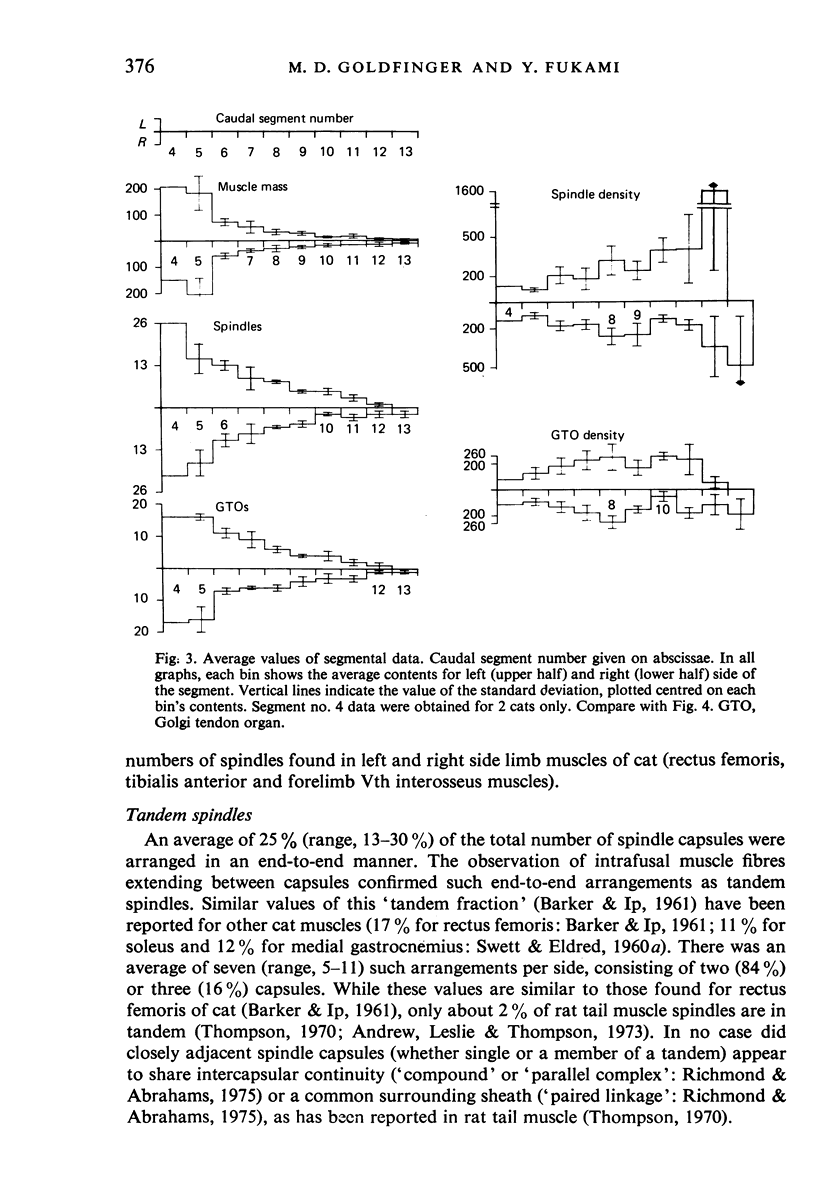
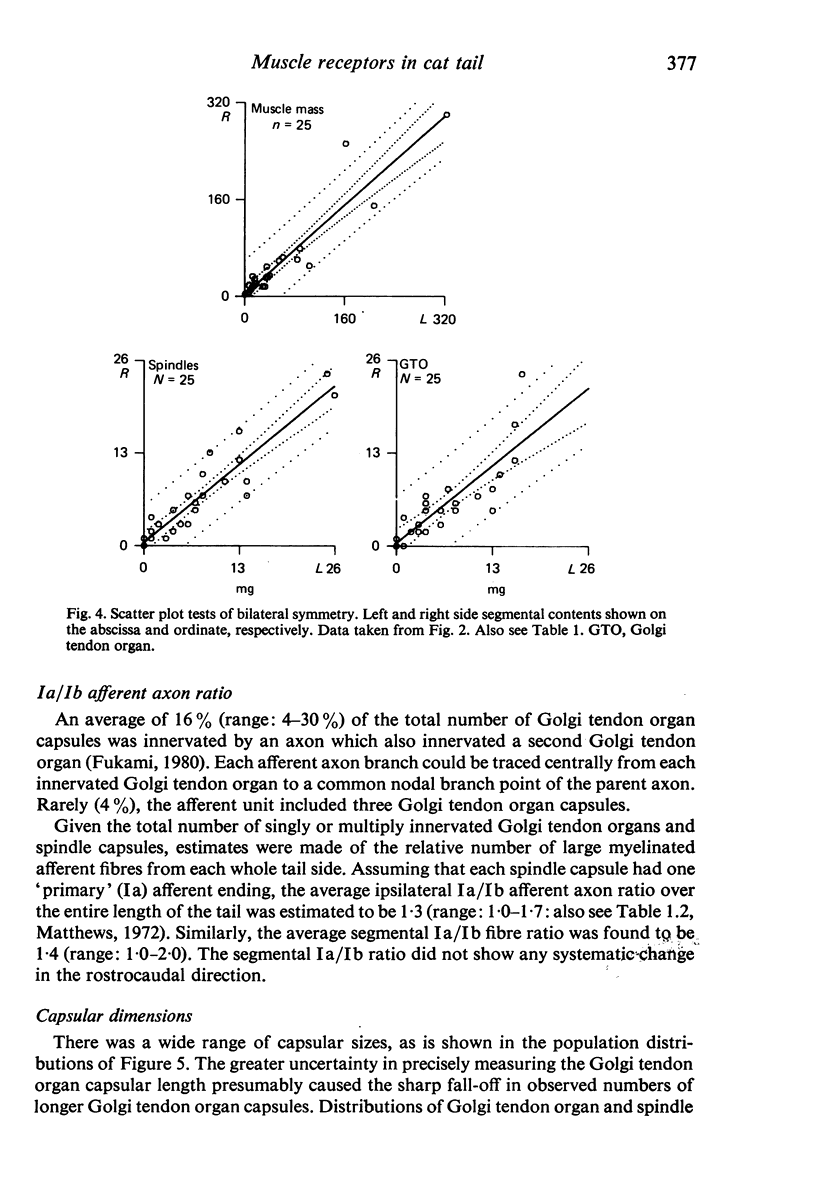
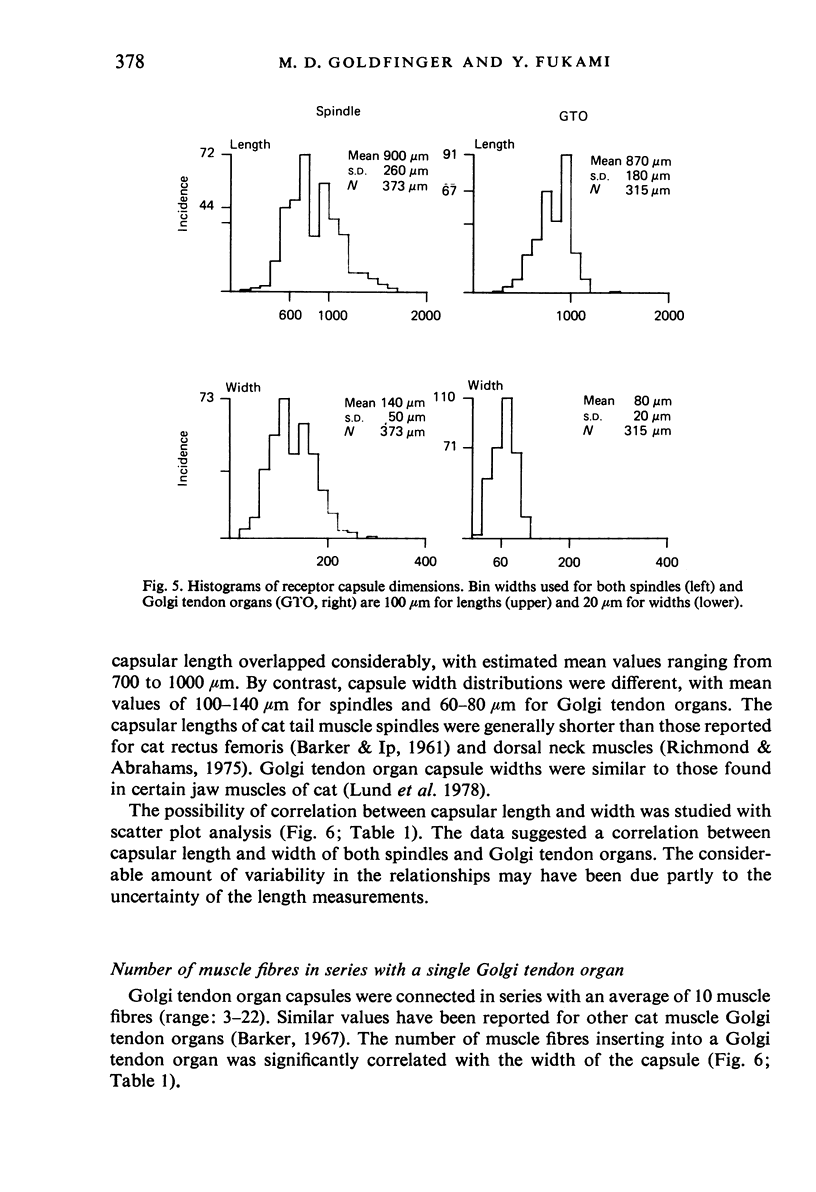





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADAL M. N., BARKER D. INTRAMUSCULAR BRANCHING OF FUSIMOTOR FIBRES. J Physiol. 1965 Mar;177:288–299. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrew B. L., Leslie G. C., Thompson J. Distribution and properties of muscle spindles in the caudal segmental muscles of the rat together with some comparisons with hind limb muscle spindles. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1973 Jan;58(1):19–37. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1973.sp002188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARKER D., CHIN N. K. The number and distribution of muscle-spindles in certain muscles of the cat. J Anat. 1960 Oct;94:473–486. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARKER D., IP M. C. A study of single and tandem types of muscle-spindle in the cat. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1961 Jul 25;154:377–397. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1961.0038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker D. A., Richmond F. J. Distribution of receptors around neck vertebrae in the cat [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1980 Jan;298:40P–41P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder M. D., Kroin J. S., Moore G. P., Stuart D. G. The response of Golgi tendon organs to single motor unit contractions. J Physiol. 1977 Oct;271(2):337–349. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukami Y. Interaction of impulse activities originating from individual Golgi tendon organs innervated by branches of a single axon. J Physiol. 1980 Jan;298:483–499. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukami Y., Wilkinson R. S. Responses of isolated Golgi tendon organs of the cat. J Physiol. 1977 Mar;265(3):673–689. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladden M. H. Muscle spindle innervation in the intertransverse caudal muscles of the rat. Experientia. 1969 Jun 15;25(6):604–606. doi: 10.1007/BF01896539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon A. M., Huxley A. F., Julian F. J. Tension development in highly stretched vertebrate muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1966 May;184(1):143–169. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houk J., Henneman E. Responses of Golgi tendon organs to active contractions of the soleus muscle of the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1967 May;30(3):466–481. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.3.466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt C. C., Ottoson D. Initial burst of primary endings of isolated mammalian muscle spindles. J Neurophysiol. 1976 Mar;39(2):324–330. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.2.324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt C. C., Ottoson D. Responses of primary and secondary endings of isolated mammalian muscle spindles to sinusoidal length changes. J Neurophysiol. 1977 Sep;40(5):1113–1120. doi: 10.1152/jn.1977.40.5.1113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt C. C., Wilkinson R. S. An analysis of receptor potential and tension of isolated cat muscle spindles in response to sinusoidal stretch. J Physiol. 1980 May;302:241–262. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt C. C., Wilkinson R. S., Fukami Y. Ionic basis of the receptor potential in primary endings of mammalian muscle spindles. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Jun;71(6):683–698. doi: 10.1085/jgp.71.6.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund J. P., Richmond F. J., Touloumis C., Patry Y., Lamarre Y. The distribution of Golgi tendon organs and muscle spindles in masseter and temporalis muscles of the cat. Neuroscience. 1978;3(2):259–270. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(78)90107-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchand R., Bridgman C. F., Shumpert E., Eldred E. Association of tendon organs with spindles in muscles of the cat's leg. Anat Rec. 1971 Jan;169(1):23–32. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091690103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer-Lohmann J., Riebold W., Robrecht D. Mechanical influence of the extrafusal muscle on the static behaviour of deefferented primary muscle spindle endings in cat. Pflugers Arch. 1974;352(3):267–278. doi: 10.1007/BF00590491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond F. J., Abrahams V. C. Morphology and distribution of muscle spindles in dorsal muscles of the cat neck. J Neurophysiol. 1975 Nov;38(6):1322–1339. doi: 10.1152/jn.1975.38.6.1322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWETT J. E., ELDRED E. Comparisons in structure of stretch receptors in medial gastrocnemius and soleus muscles of the cat. Anat Rec. 1960 Aug;137:461–473. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091370406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWETT J. E., ELDRED E. Distribution and numbers of stretch rceptors in medial gastrocnemius and soleus muscles of the cat. Anat Rec. 1960 Aug;137:453–460. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091370405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. Parallel spindle systems in the small muscles of the rat tail. J Physiol. 1970 Dec;211(3):781–799. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellin H. A histochemical study of muscle spindles and their relationship to extrafusal fiber types in the rat. Am J Anat. 1969 May;125(1):31–45. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001250103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]