Abstract
1. Rats were infused in vivo with [U-14C]glycine for periods of 2–6h, during which time the specific radioactivity of the free glycine in plasma and tissue approached a constant value. 2. Free serine also became labelled. The ratio of specific radioactivity of serine to that of glycine in the protein of liver, kidney, brain, jejunum, heart, diaphragm and gastrocnemius muscle was closer to the ratio in the free amino acid pool of the tissue than that of the plasma. 3. The kinetics of incorporation of [14C]glycine and [14C]serine into the protein of gastrocnemius muscle further suggested that the plasma free amino acids were not the immediate precursors of protein. 4. Infusion of rats with [U-14C]serine resulted in labelling of free glycine. The ratio of specific radioactivity of glycine to serine in the protein of liver, kidney, brain, jejunum and heart again suggested incorporation from a pool similar to the free amino acid pool of the tissue. 5. Rates of tissue protein synthesis calculated from the incorporation into protein of both radioactive glycine and serine, either infused or derived, were very similar when the precursor specific radioactivity was taken to be that in the total free amino acids of the tissue. Except for gastrocnemius muscle and diaphragm during the infusion of radioactive serine, the rates of tissue protein synthesis calculated from the specific radioactivity of the free glycine and serine in plasma differed markedly.
Full text
PDF
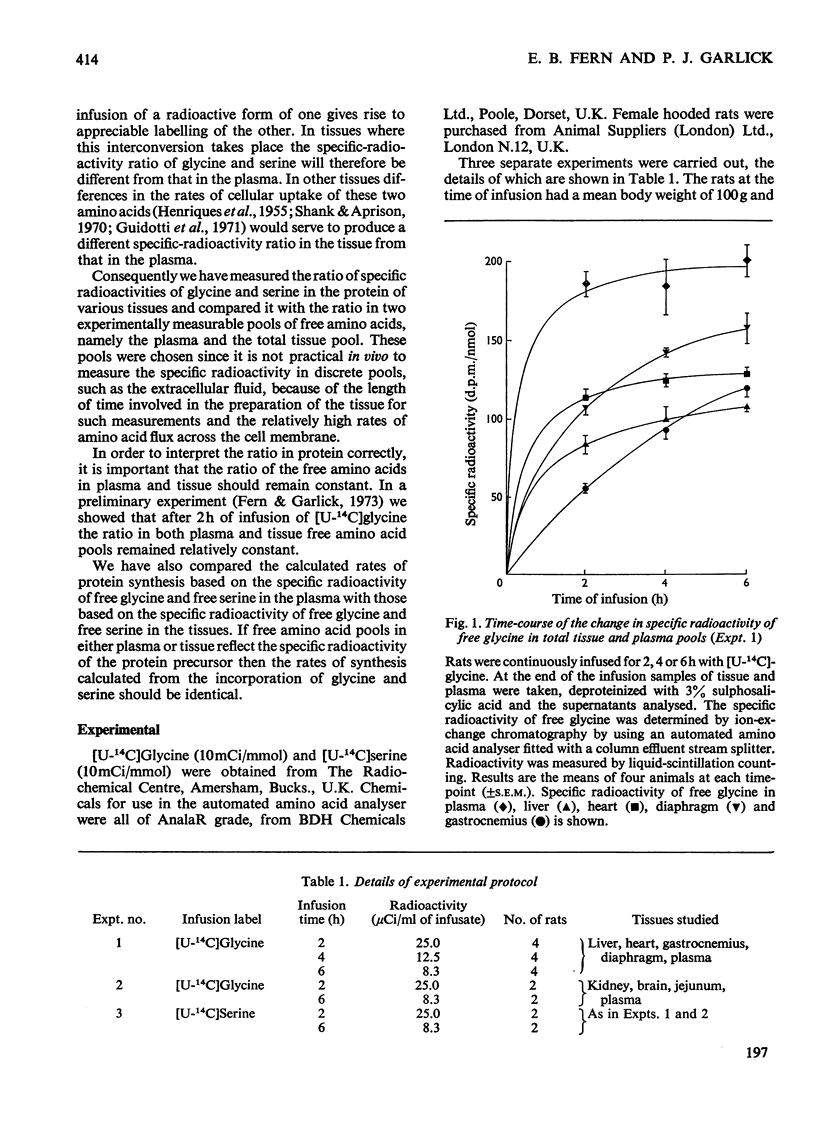
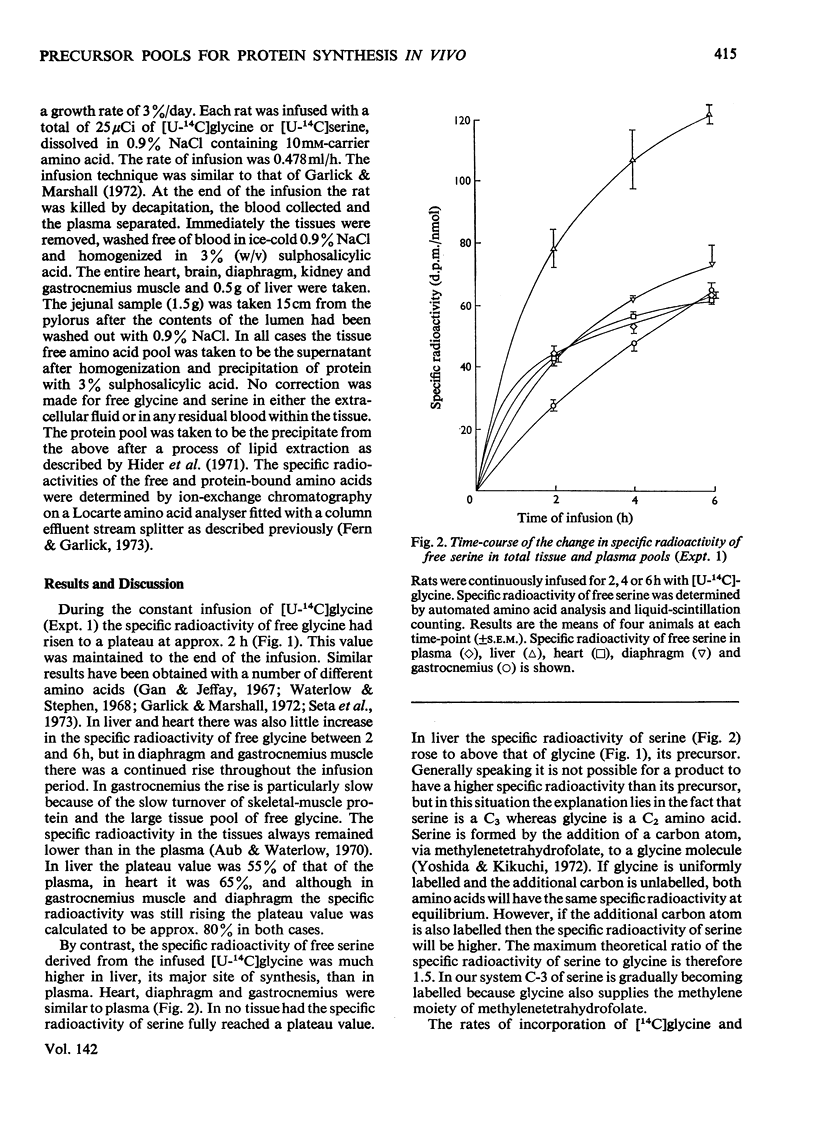
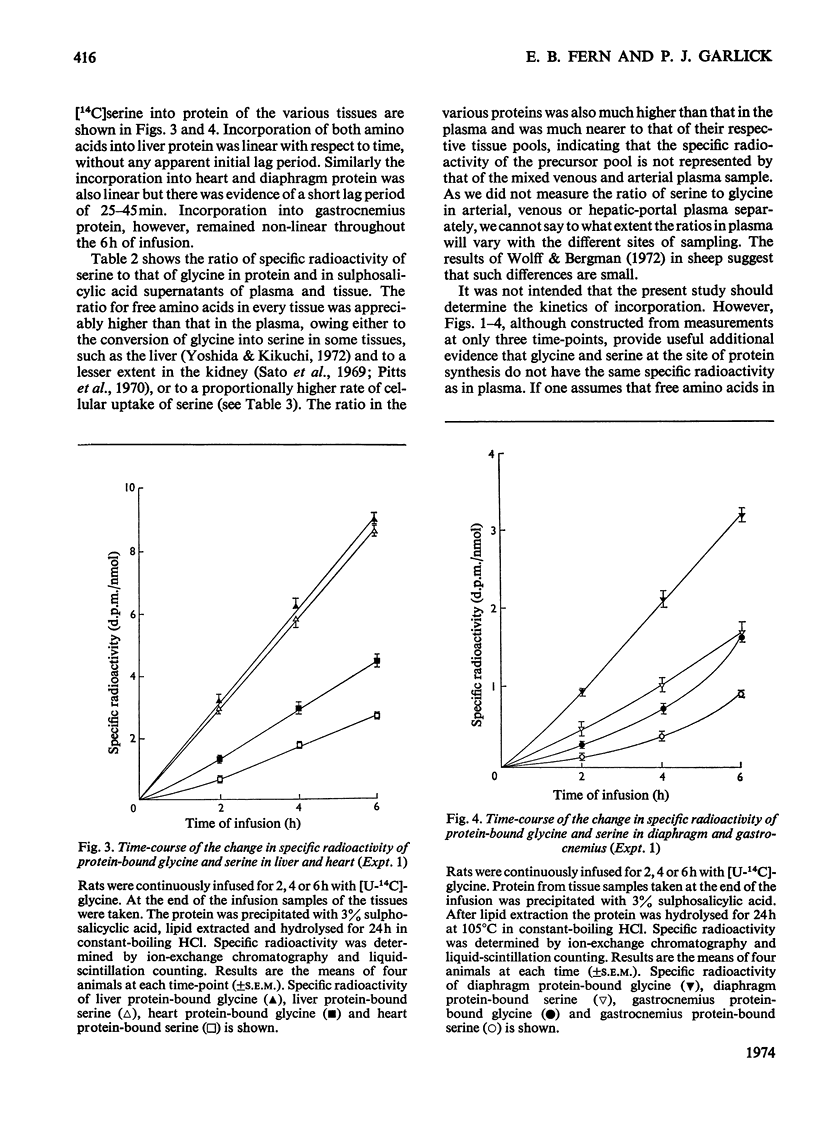
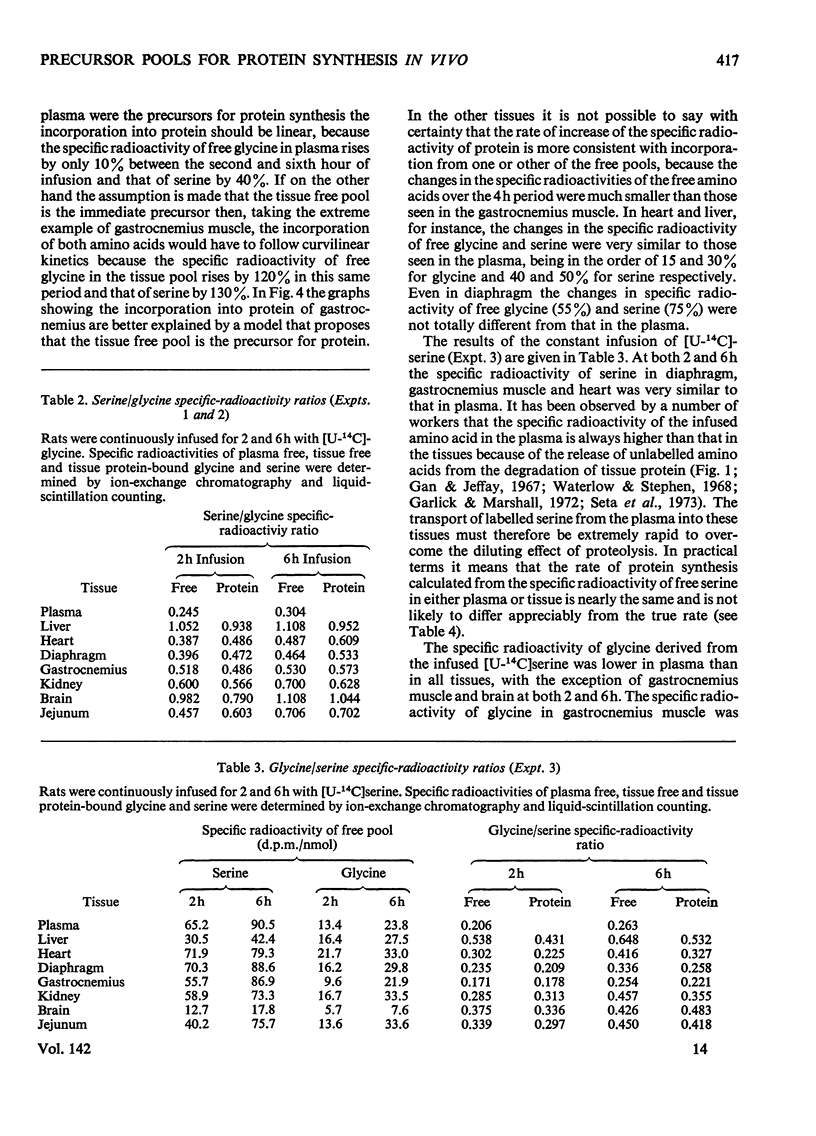


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson L. F., Herington A. C., Bornstein J. Evidence for the selection by the membrane transport system of intracellular or extracellular amino acids for protein synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 1;282(1):352–365. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90340-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aub M. R., Waterlow J. C. Analysis of a five-compartment system with continuous infusion and its application to the study of amino acid turnover. J Theor Biol. 1970 Feb;26(2):243–250. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(70)80015-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earl D. C., Korner A. Effect of actinomycin on cardiac ribosomes and polysomes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Sep 9;115(3):437–444. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90061-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fern E. B., Garlick P. J. The specific radioactivity of the precursor pool for estimates of the rate of protein synthesis. Biochem J. 1973 Aug;134(4):1127–1130. doi: 10.1042/bj1341127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gan J. C., Jeffay H. Origins and metabolism of the intracellular amino acid pools in rat liver and muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Nov 28;148(2):448–459. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90141-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garlick P. J., Marshall I. A technique for measuring brain protein synthesis. J Neurochem. 1972 Mar;19(3):577–583. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01375.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garlick P. J., Millward D. J., James W. P. The diurnal response of muscle and liver protein synthesis in vivo in meal-fed rats. Biochem J. 1973 Dec;136(4):935–945. doi: 10.1042/bj1360935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garlick P. J. Turnover rate of muscle protein measured by constant intravenous infusion of 14C-glycine. Nature. 1969 Jul 5;223(5201):61–62. doi: 10.1038/223061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti G. G., Borghetti A. F., Lüneburg B., Gazzola G. C. Kinetic analysis of insulin action on amino acid uptake by isolated chick embryo heart cells. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(4):409–414. doi: 10.1042/bj1220409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENDLER R. W. A model for protein synthesis. Nature. 1962 Mar 3;193:821–823. doi: 10.1038/193821a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENRIQUES O. B., HENRIQUES S. B., NEUBERGER A. Quantitative aspects of glycine metabolism in the rabbit. Biochem J. 1955 Jul;60(3):409–424. doi: 10.1042/bj0600409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hider R. C., Fern E. B., London D. R. Identification in skeletal muscle of a distinct extracellular pool of amino acids, and its role in protein synthesis. Biochem J. 1971 Mar;121(5):817–827. doi: 10.1042/bj1210817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hider R. C., Fern E. B., London D. R. Relationship between intracellular amino acids and protein synthesis in the extensor digitorum longus muscle of rats. Biochem J. 1969 Sep;114(2):171–178. doi: 10.1042/bj1140171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIPNIS D. M., REISS E., HELMREICH E. Functional heterogeneity of the intracellular amino acid pool in mammalian cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Aug 19;51:519–524. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90608-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. B., Fulks R. M., Goldberg A. L. Evidence that the intracellular pool of tyrosine serves as precursor for protein synthesis in muscle. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 25;248(20):7272–7275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANCHESTER K. L., WOOL I. G. INSULIN AND INCORPORATION OF AMINO ACIDS INTO PROTEIN OF MUSCLE. 1. ACCUMULATION AND INCORPORATION STUDIES WITH THE PERFUSED RAT HEART. Biochem J. 1963 Nov;89:202–209. doi: 10.1042/bj0890202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millward D. J., Garlick P. J. The pattern of protein turnover in the whole animal and the effect of dietary variations. Proc Nutr Soc. 1972 Dec;31(3):257–263. doi: 10.1079/pns19720049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan H. E., Earl D. C., Broadus A., Wolpert E. B., Giger K. E., Jefferson L. S. Regulation of protein synthesis in heart muscle. I. Effect of amino acid levels on protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):2152–2162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimore G. E., Woodside K. H., Henry J. E. Compartmentation of free valine and its relation to protein turnover in perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2776–2784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitts R. F., Damian A. C., MacLeod M. B. Synthesis of serine by rat kidney in vivo and in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1970 Sep;219(3):584–589. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.3.584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENBERG L. E., BERMAN M., SEGAL S. Studies of the kinetics of amino acid transport, incorporation into portein and oxidation in kidney-cortex slices. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Jun 4;71:664–675. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91140-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Righetti P., Little E. P., Wolf G. Reutilization of amino acids in protein synthesis in HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 25;246(18):5724–5732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato T., Kochi H., Motokawa Y., Kawasaki H., Kikuchi G. Glycin metabolism by rat liver mitochondria. I. Synthesis of two molecules of glycine from one molecule each of serine, bicarbonate and ammonia. J Biochem. 1969 Jan;65(1):63–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seta K., Sansur M., Lajtha A. The rate of incorporation of amino acids into brain proteins during infusion in the rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 4;294(1):472–480. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90103-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shank R. P., Aprison M. H. The metabolism in vivo of glycine and serine in eight areas of the rat central nervous system. J Neurochem. 1970 Oct;17(10):1461–1475. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1970.tb00513.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner L. V., Garlick P. J. The effect of unilateral phrenicectomy on the rate of protein synthesis in rat diaphragm in vivo. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Apr 27;349(1):109–113. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Venrooij W. J., Poort C., Kramer M. F., Jansen M. T. Relationship between extracellular amino acids and protein synthesis in vitro in the rat pancreas. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Nov 7;30(3):427–433. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02114.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterlow J. C., Stephen J. M. The effect of low protein diets on the turn-over rates of serums, liver and muscle proteins in the rat, measured by continuous infusion of L-[14C]lysine. Clin Sci. 1968 Oct;35(2):287–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler K. Protein synthesis in human leucocytes. 3. Kinetics of the flow of amino acids from the extracellular space and the intracellular pools resulting in protein synthesis. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1972 May;353(5):782–786. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1972.353.1.782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff J. E., Bergman E. N. Metabolism and interconversions of five plasma amino acids by tissues of the sheep. Am J Physiol. 1972 Aug;223(2):447–454. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.2.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woll I. G., Stirewalt W. S., Moyer A. N. Effect of diabetes and insulin on nucleic acid metabolism of heart muscle. Am J Physiol. 1968 Apr;214(4):825–831. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.4.825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida T., Kikuchi G. Comparative study on major pathways of glycine and serine catabolism in vertebrate livers. J Biochem. 1972 Dec;72(6):1503–1516. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Venrooij W. J., Kuijper-Lenstra A. H., Kramer M. F. Interrelationship between amino acid pools and protein synthesis in the rat submandibular gland. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 23;312(2):392–398. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90383-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


