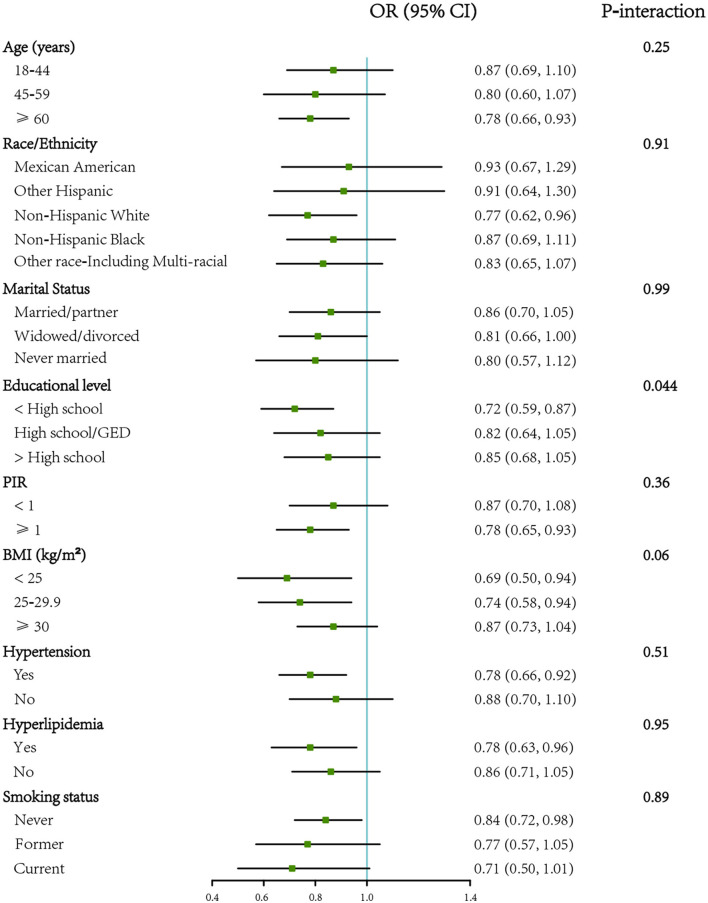
Figure 3.
Forest plot showing the associations of VB2 intake with diabetes by different characteristics in women (n = 9,469). OR (95% CI) are reported per 1-SD increment of log-transformed vitamin B2 intake. The models were adjusted for age (18–44, 45–59, or ≥60 years), energy intake (continuous), race/ethnicity (Mexican American, other Hispanic, non-Hispanic White, non-Hispanic Black, or other Race-Including Multi-racial), marital status (married/partner, widowed/divorced, or never married), educational level (<high school, high school/GED, or >high school), PIR (<1 or ≥1), BMI (<25, 25–29.9, or ≥30 kg/m2), hypertension (yes or no), hyperlipidemia. BMI, body mass index; GED, General Educational Development; PIR, ratio of family income to poverty. SD, standard deviation.