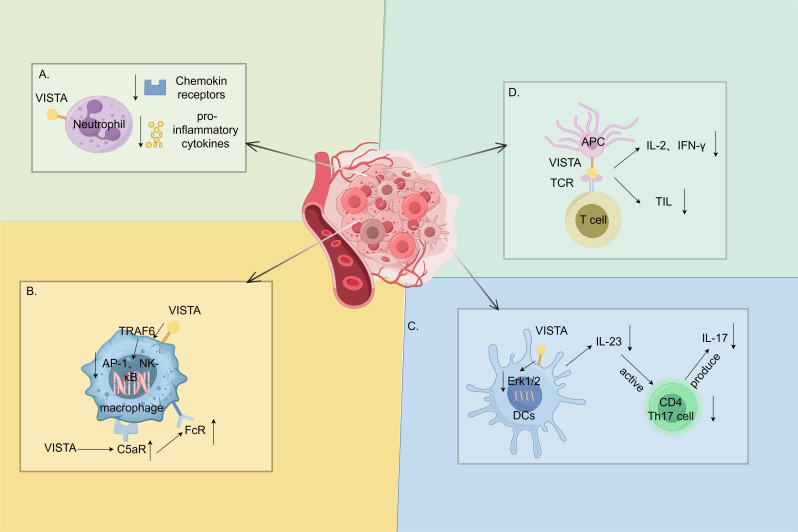
Figure 3.
Immune function of the V-domain Ig suppressor of T-cell activation (VISTA) highly expressed in myeloid cells. (A). The V-domain Ig suppressor of T-cell activation (VISTA) in neutrophils suppresses inflammation by decreasing the chemokine receptor and the pro-inflammatory cytokine expression (34). (B). VISTA has a dual role in macrophages. On the one hand, it inhibits the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines through the MAPKs/AP-1 and IKKα/β/NF-κB signaling pathways (11). On the other hand, it ensures the expression of C5a receptors on the macrophage surface in mice, which forms immune complexes and promotes inflammatory responses (35). (C). VISTA, which has a regulatory role in the IL-23/IL-17 axis, regulates the IL-23 production in dendritic cells (DCs) by attenuating the ErK1/2 activation. It subsequently inhibits the CD4 T helper lymphocyte 17 (Th17) activation and the IL-17 production (36). (D). Interactions with APCs and T cells inhibit antigen-specific T-cell activation (5) and reduce the IL-2 and IFN-γ production, as well as the number of tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells (37). MAPKs, mitogen-activated protein kinases; AP-1, activator protein 1; IKK, IKB kinase complex; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B. (By Figdraw).