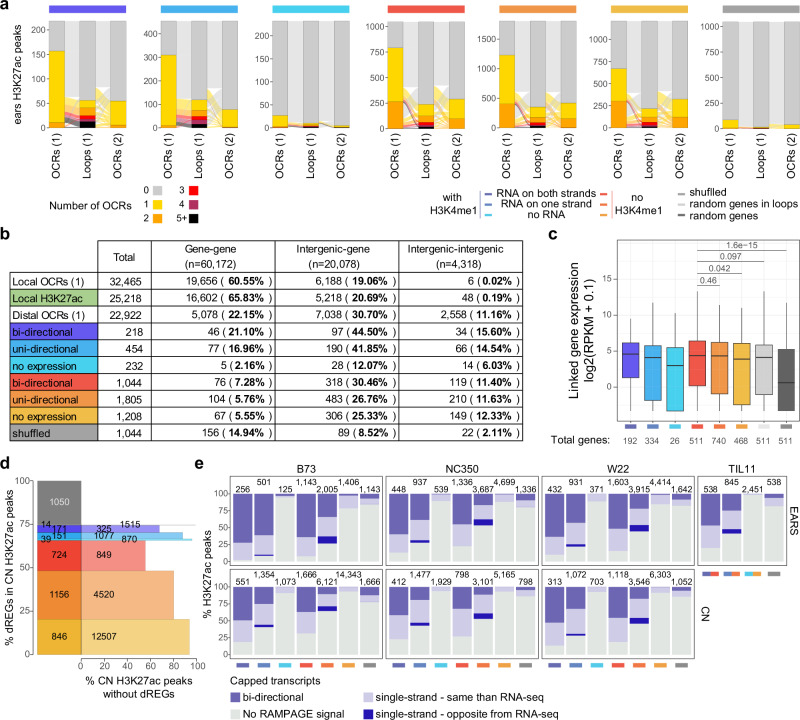
Fig. 6. Enhancer RNA-expressing regions are enriched in chromatin loops.
a Alluvial plots showing the number of open chromatin regions (OCRs) intersecting H3K27ac peaks, split by the presence of H3K4me1 peak within 1 kb, and the presence of RNA within the peaks. H3K27ac peaks identified in B73 immature ears were compared to OCRs from ATAC-seq and to chromatin loops from Hi-C from (1) Sun et al. 38 and to OCRs from (2) Ricci et al. 10. The highest overlap is between Sun et al. 38 OCRs and enhancers with bi-directional enhancer RNAs (eRNAs). b Table summarizing the number of enhancers found in the chromatin loop anchors identified by Hi-C38. H3K27ac peaks within 2 kb of a gene body (local H3K27ac, green) are more often in a loop than local OCRs. Distal H3K27ac peaks are included in intergenic loops to similar levels than OCRs. The presence of H3K4me1 however increases the percentage of these regions to be within loops, which support their classification as misannotated genes. c Expression level in immature ears (log2(RPKM + 0.1)) of the genes linked by chromatin loops to the different types of enhancers described in (a). Genes linked to enhancers with bi-directional eRNAs are more highly expressed than random genes, but marginally more highly expressed than random genes in loops (two-sided t test). d Intersection between elements with bi-directional nascent transcripts identified by discriminative regulatory-element (dREGs) in maize GRO-seq data33 and H3K27ac peaks in the coleoptilar node (CN). e Percentage of H3K27ac peaks with RAMPAGE signal, in immature ears and CN of each inbred. From 30 to 70% of enhancer RNAs are capped in bi-directional enhancers, while 10 to 30% of enhancers with stranded RNA-seq transcripts also have bi-directional RAMPAGE signal, suggesting an underestimation of the total number of bi-directional enhancers.