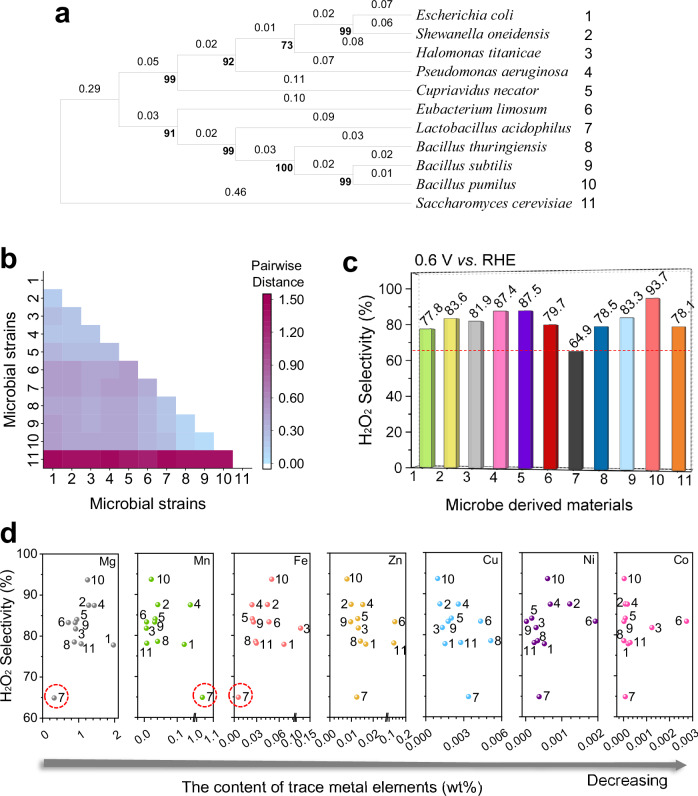
Fig. 1. Evaluation of microbe-derived electrocatalysts for H2O2 production.
a Molecular phylogenetic analysis of 16S (and 18S of Saccharomyces cerevisiae) rRNA gene sequences using the maximum likelihood method. b Genetic distances of amino acid sequences determined using the Poisson correction model. c H2O2 selectivity of various microbe-derived electrocatalysts. d, Relationships between the contents of metal elements in microbe-derived electrocatalysts and their H2O2 selectivity. The numerical ordinal numbers accompanying the strain names in (a) correspond to the microbial strains and their derived carbon materials in (b, d), respectively. During the electrochemical measurements, 85% iR compensation was applied.