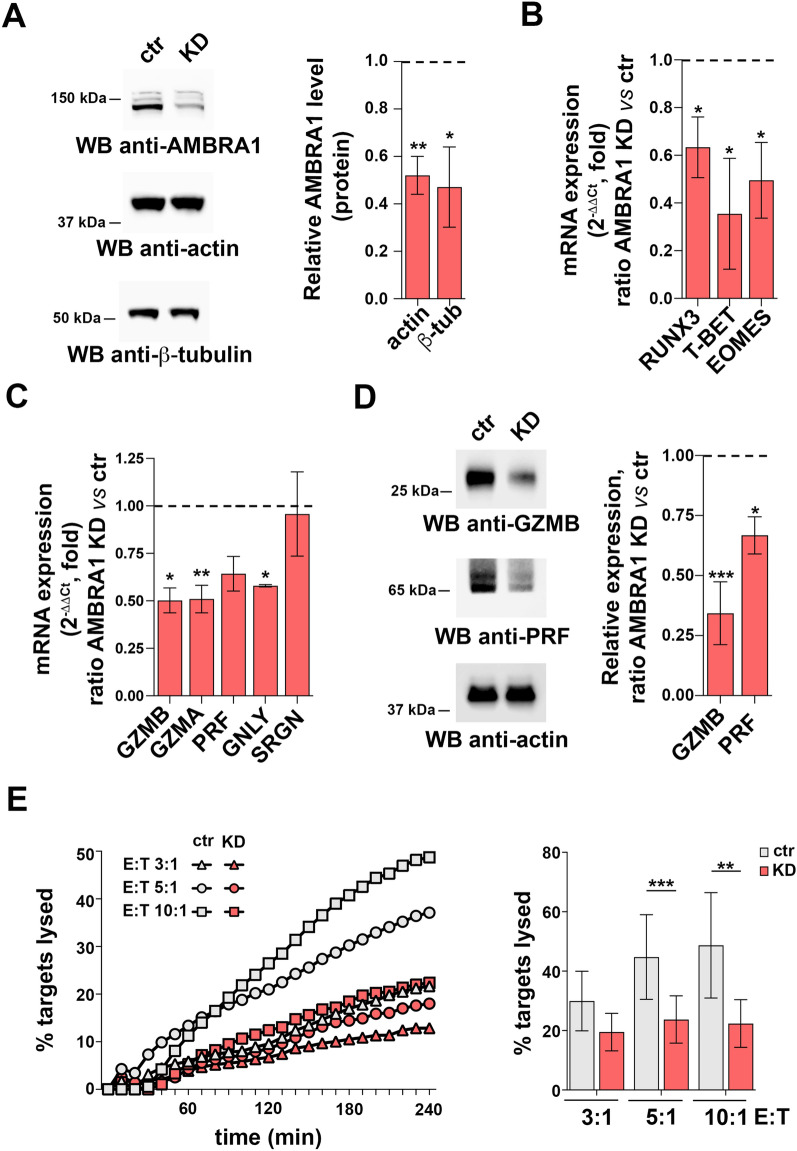
Fig. 2.
AMBRA1 is required for CD8+ T cell differentiation to CTLs. (A) Immunoblot analysis of human AMBRA1 levels in control (ctr, scramble RNAi) and AMBRA1 KD CTLs (KD). Actin and ß-tubulin were used as loading controls. The migration of molecular mass markers is indicated. The histogram shows the quantification of AMBRA1 expression in CTLs normalized to actin or ß-tubulin (n = 3, one sample t test, ctr value = 1). (B) RT-qPCR analysis of human RUNX3, T-BET and EOMES mRNA in control and AMBRA1 KD CTLs. 18S was used for normalization (ndonor = 3, one sample t test, ctr value = 1). (C) RT-qPCR analysis of the GZMA, GZMB, PRF, GNLY and SRGN mRNA and (D) Immunoblot analysis of the LG components GZMB and PRF in control and AMBRA1 KD CTLs. Actin was used as loading control. The migration of molecular mass markers is indicated. The histogram shows the quantification of GZMB and PRF expression in AMBRA1 KD CTLs related to control CTLs (n = 3, one sample t test, ctr value = 1). (E) Real-time calcein release-based killing assay. Control or AMBRA1 KD CTLs were co-cultured with sAg-loaded Raji B cells at the target:effector (T:E) ratios indicated. The graph shows the kinetics of target cell killing quantified by measuring calcein fluorescence every 10 min for 4 h. The histogram shows the quantification of the percentage of target cell death at the endpoint (4 h) of independent experiments carried out on CTLs from ndonor = 3, performed in duplicate (one-way ANOVA test). Data are shown as mean fold ± SD. * P ≤ 0.05; ** P ≤ 0.01; *** P ≤ 0.001; **** P ≤ 0.0001.