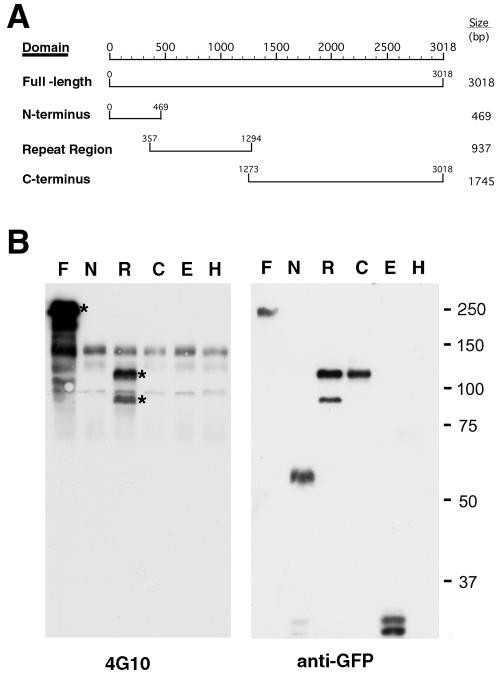
FIG. 1.
Ectopic expression of C. trachomatis GFP-Tarp domains indicates tyrosine phosphorylation of the repeat region of Tarp. (A) Schematic of the C. trachomatis L2 Tarp domains expressed as C-terminal GFP fusions. (B) Immunoblots of protein extracts from HeLa 229 cells transfected with the various enhanced GFP (EGFP) fusion constructs. F, full-length Tarp; N, N-terminal domain; R, repeat region; C, C-terminal domain; E, EGFP vector control; H, uninfected HeLa cells. Blots were probed with MAb 4G10 for tyrosine phosphorylation and anti-GFP to confirm expression and relative migration. Asterisks identify tyrosine phosphorylation of TARP and the repeat region. An apparent degradation product of the repeat region is also detected. Please note that the repeat region fusion migrates aberrantly on SDS-PAGE, as does native Tarp (11). The same Kpn-Bam insert was also cloned into pRsetB for expression in E. coli, and the product was confirmed as the Tarp repeat region by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectroscopy (data not shown). Background tyrosine-phosphorylated host protein bands seen in HeLa cells are apparent in all lanes probed with MAb 4G10.