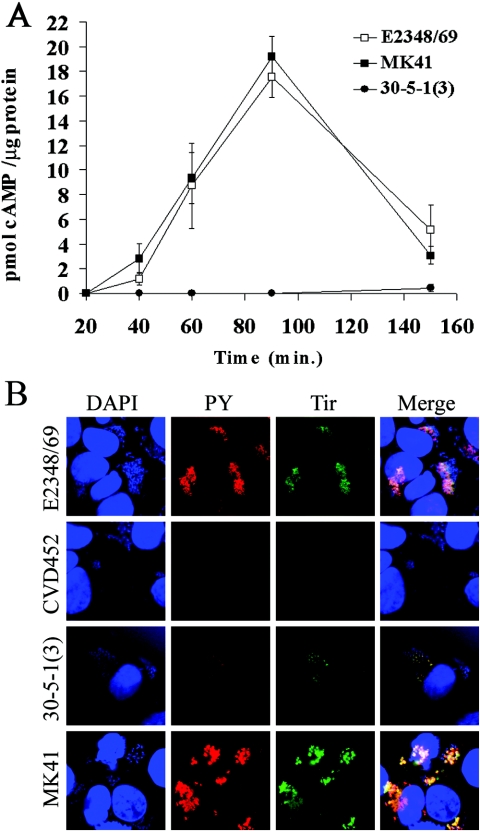
FIG. 3.
Analysis of Tir translocation and tyrosine phosphorylation by sepZ mutant EPEC strains. (A) Kinetic analysis of Tir-CyaA translocation. E2348/69 (wild type), MK41 (ΔsepZ), and 30-5-1(3) (sepZ::TnphoA) containing pAC115(Tir-CyaA) were each used to infect HeLa cells at a multiplicity of infection of 100:1 (EPEC:HeLa cell) for 20, 40, 60, 90, and 150 min. At the times indicated, lysates were prepared, and cAMP amounts were measured by a cAMP EIA. The geometric mean and standard deviation for three independent infections are represented. (B) Tir and phosphotyrosine immunofluorescence confocal microscopy of HeLa cells infected with E2348/69 (wild type), CVD451 (escN), MK41 (ΔsepZ), and 30-5-1(3) (sepZ::TnphoA). Cells were colabeled with DAPI (blue), mouse anti-phosphotyrosine monoclonal antibody was detected by AlexaFluor 568 goat anti-mouse antibody (PY; red), and polyclonal rabbit anti-Tir antisera was detected with AlexaFluor 488 goat anti-rabbit antibody (green). The corresponding images of DNA, phosphotyrosine, and Tir were combined (Merge).