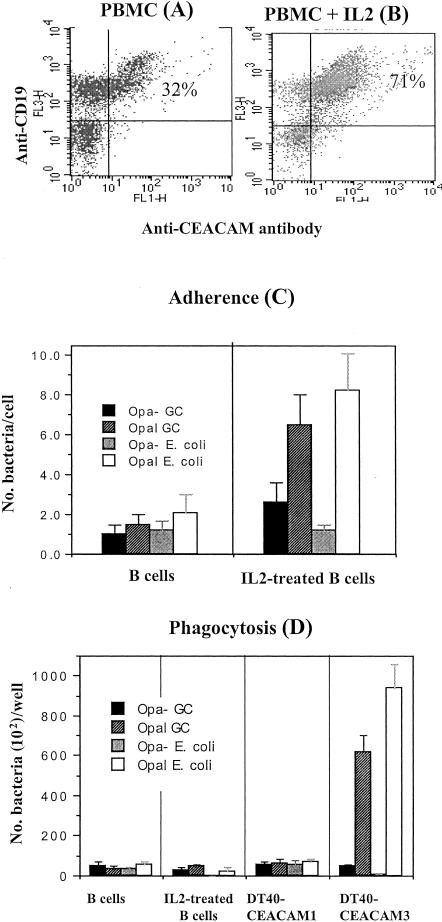
FIG. 1.
The increasing expression of CEACAM1 in human B cells involves IL-2 and results in the enhancement of adherence to Opa+ bacteria. Human PBMC were treated with IL-2 for 3 days. The expression level of CEACAM on B cells was determined with flow cytometry by double staining of B cells with allophycocyanin-anti-CD19 (F3) and FITC-anti-CEACAM (F1) antibodies. (A and B) PBMC with and without IL-2 treatment. The top right section contains CEACAM1-expressing B cells. The adherence and invasion of GC and E. coli with purified B cells were determined by direct counting of the number of bacteria per cell (C) and by recovery of CFU after treatment with gentamicin (D), respectively. DT40-CEACAM1 and DT40-CEACAM3 cells serve as control cell lines.