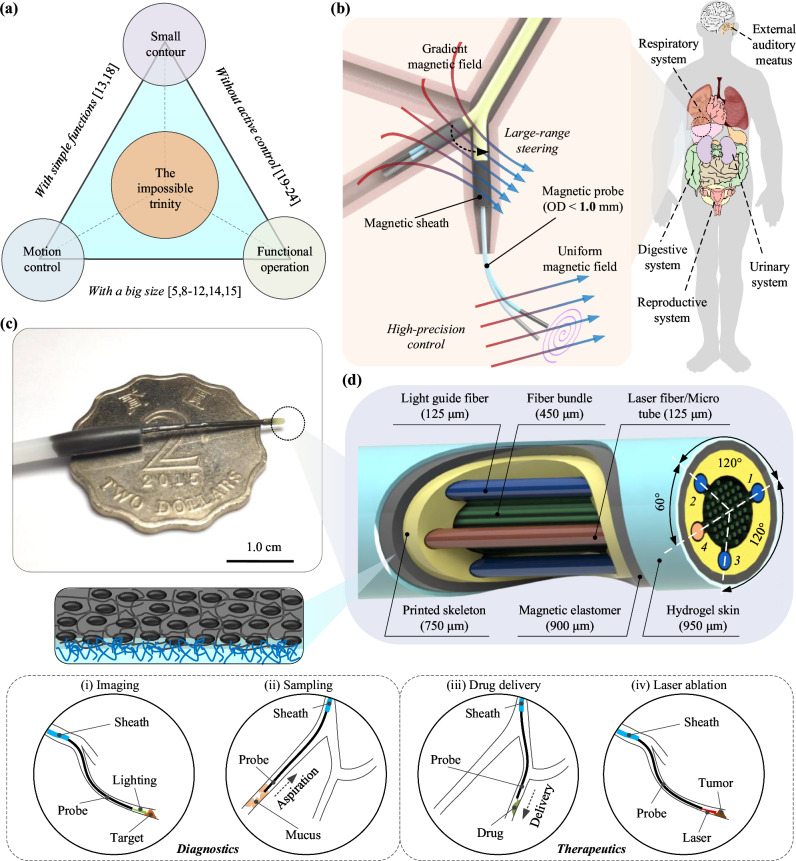
Fig. 1. Overview of the optical fiber-based sub-millimeter continuum robot with imaging, maneuvering, and medical operation capabilities.
a Achieving small contour, high-precision motion control, and visualized functional operations simultaneously poses a challenge for robots, referred to as the “impossible trinity”. b Schematics of the proposed sub-millimeter continuum robot driven by multi-sectional magnetic fields for medical diagnosis and treatment in narrow channels. c Image depicting the probe tip, over a two-dollar Hong Kong coin. d Schematic of the probe tip, comprising of a central fiber bundle, three light guide fibers (No. 1, 2, 3), and an additional functional tool channel (No. 4) within the skeleton fabricated by microscale 3D printing technology. A thin layer of magnetic elastomer is coated on the probe for actuation, and then a thin hydrogel layer is covered on the outer surface to reduce the friction. The manufactured probe boasts a diameter contour of 0.95 mm. The diagnostic and therapeutic potential of the fiberscopic robot include (i) imaging, (ii) sampling, (iii) drug delivery, and (iv) laser ablation.