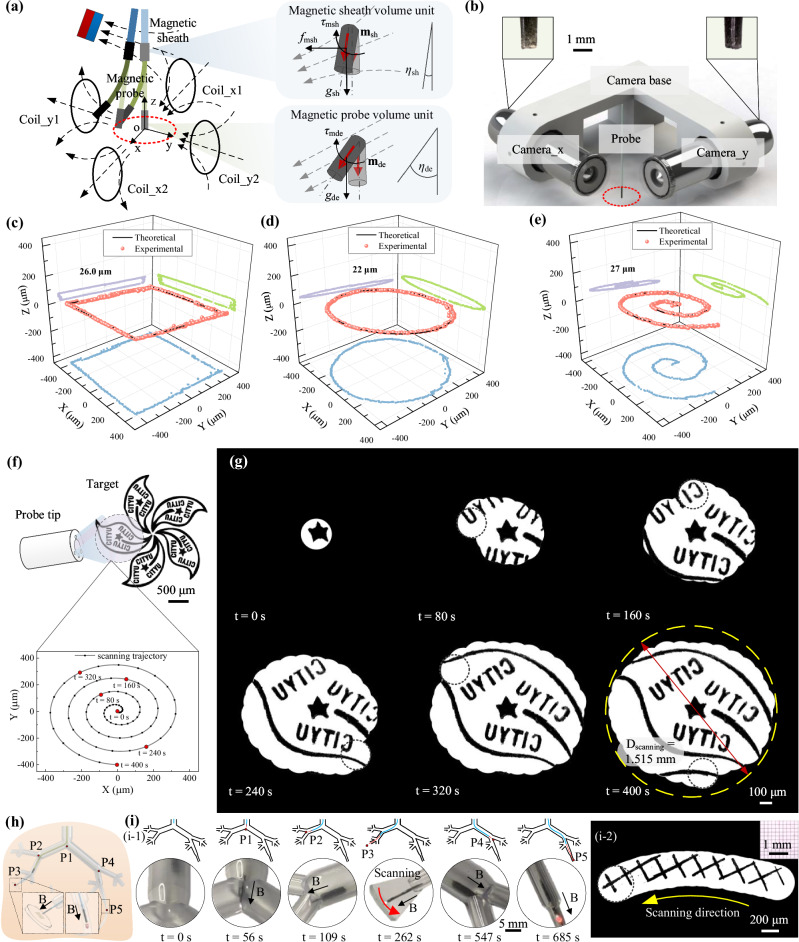
Fig. 4. High precise maneuvering of the continuum robot.
a Schematic depicting the multi-sectional actuation by the magnetic field. The magnetic sheath is actuated by a gradient magnetic field to achieve large-range steering, while the magnetic probe is actuated by a uniform magnetic field to achieve high-precision motion. b Experimental setup for evaluating the probe’s motion trajectory. Path tracking results of the probe tip under square (c), circle (d), and spiral (e) trajectories, presenting a motion error of less than 30 μm for complex 3D trajectories. The light blue, green, and purple dots here correspond to the projection in the x-o-y plane, x-o-z plane, and y-o-z plane of the recorded trajectories. f Schematic illustrating sample scanning by a designed Archimedes spiral trajectory. g Reconstruction results (one leaf of a Bauhinia flower) utilizing the local scanning and stitching strategy, achieving a ~25-fold expansion of view. h Schematic of the interventional procedure performed by the continuum robot in an in vitro bronchial tree model. i Experimental snapshot of the interventional process and the scanning result of a grid pattern. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.