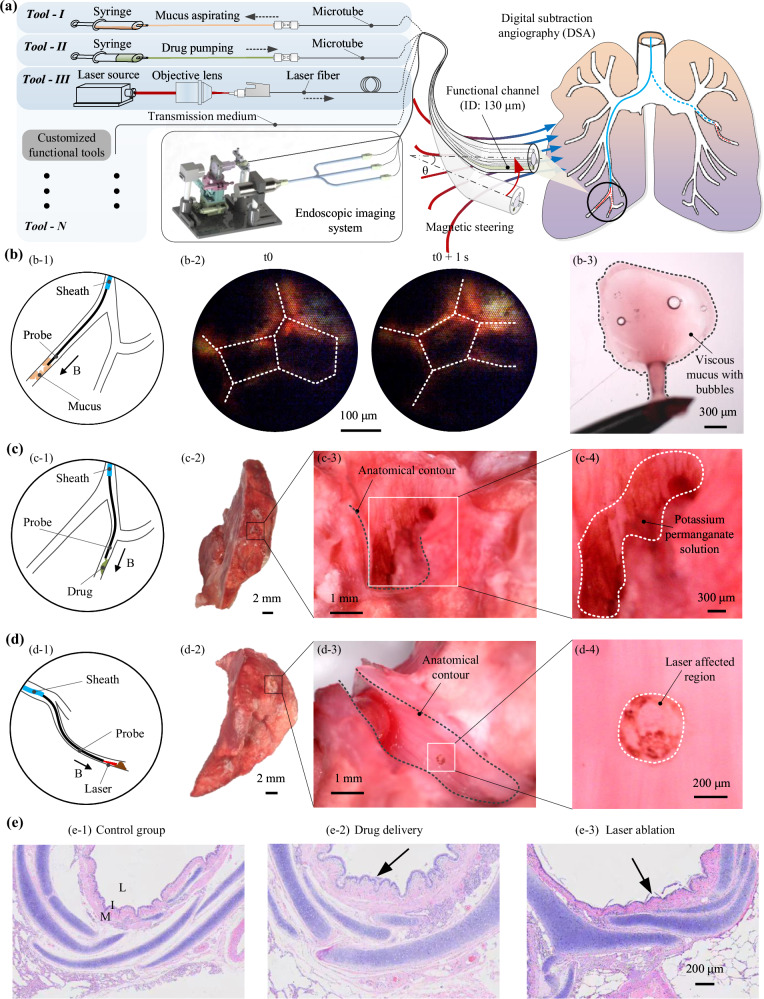
Fig. 5. Functional demonstration of the continuum robot in an ex vivo porcine model.
a Schematic illustrating the multifunctional integration of the proposed continuum robot and its demonstration in ex vivo intervention under magnetic actuation. Various functions can be achieved by integrating different types of medical tools. b Schematic representation of the mucus sampling (b-1) inside the end bronchus (ID: ~1.0 mm). The detected air bubbles by the probe suggest the existence of mucus (b-2). The aspirated sample exhibits viscous characteristic and embedded microscale bubbles (b-3), verifying endoscopic recording. Similar results can be found in repeated three times experiments. c Schematic depicting drug delivery (c-1) inside an end bronchus. Anatomical results of the end bronchus (c-2) demonstrate successful delivery of the drug (potassium permanganate solutions, brown color after oxidization) on its inner surface (c-3, 4). d Schematic of laser ablation (d-1) within an end bronchus. Anatomical examination of the bronchus (d-2) reveals ablation results (a scar of ~300 μm diameter) caused by the laser on the inner surface (d-3, 4). e H&E results further confirm the effectiveness of drug delivery and laser ablation, i.e., the deeper grooves (e-2) and the debris (e-3) show significant difference compared to normal bronchus tissue (e-1). Similar results can be found in repeated three times experiments. L, I, M denote bronchus lumen, ciliated endothelium, and muscle matrix, respectively.