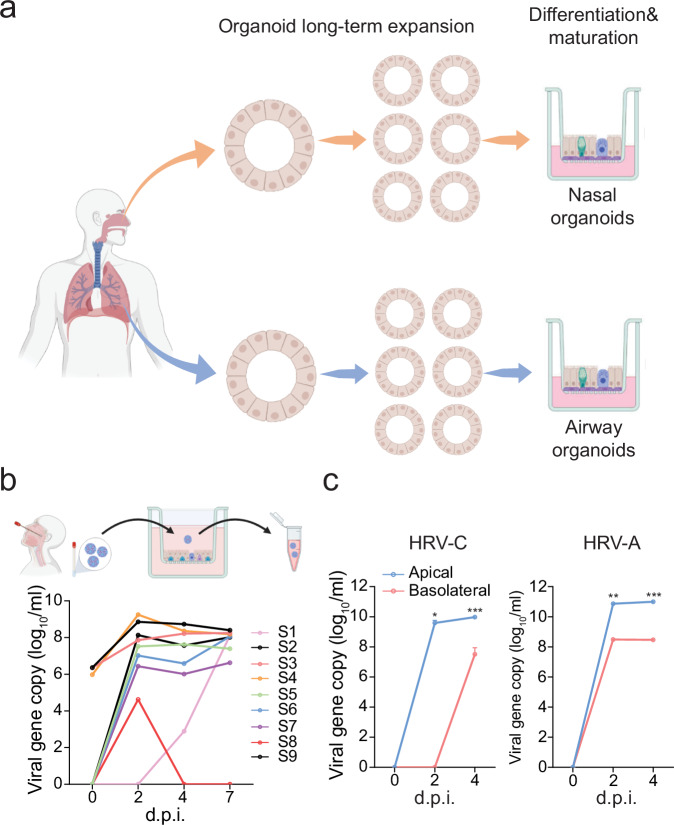
Fig. 1. Human airway organoids were susceptible to clinical specimens of HRV-C.
a A schematic illustration of the human nasal organoid and airway organoid culture system was created with Biorender.com. b Airway organoids (in 9 transwell inserts) were inoculated with 9 HRV-C+ nasopharyngeal aspirates. At the indicated day post-infection (d.p.i.), culture media were harvested from the infected airway organoids and applied to viral load detection by RT-qPCR. A schematic graph of the experimental procedure was created with Biorender.com. c Airway organoids were inoculated with HRV-A1 and HRV-C3 at 100 viral gene copy/cell (n = 3). Culture media were harvested from apical and basolateral chambers of infected airway organoids at the indicated d.p.i. and applied to the viral load detection. Data represent mean and SD of the indicated number (n) of biological replicates from a representative experiment independently performed three times. Statistical significance (in panel c) was determined using a two-tailed Student’s t-test. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.