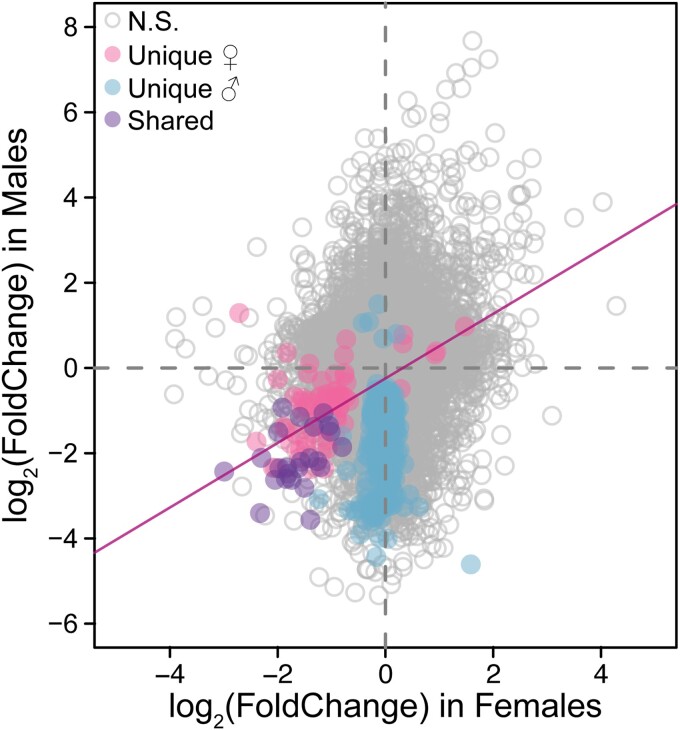
Fig. 2.
A comparison of changes in gene expression levels between females and males. Positive expression changes correspond to upregulation in evolved females/males, while negative expression changes correspond to downregulation in evolved females/males. Genes that are not significantly differentially expressed in either sex are shown in gray. Genes that are significantly differentially expressed in males but not in females (i.e. unique male) are shown in blue. Genes that are significantly differentially expressed in females but not in males (i.e. unique female) are shown in pink. Genes that are significantly differentially expressed in both sexes (i.e. shared) are shown in purple. There is a significant relationship between the change in gene expression in females and males for all female DEs (F1,98 = 42.16, P < 0.001, adjusted R2 = 0.29).