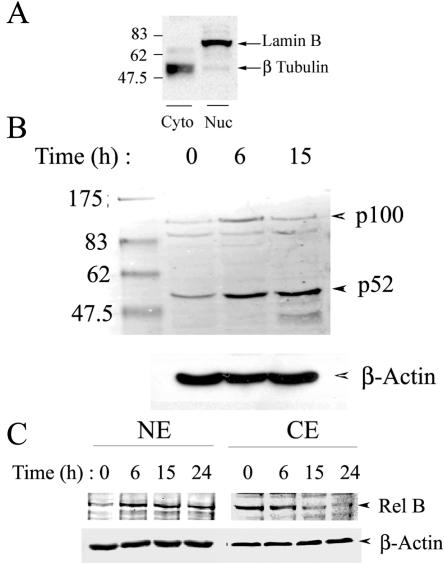
FIG. 3.
Effect of RSV infection on the noncanonical NF-κB activation pathway in A549 cells. (A) Western immunoblot for nuclear and cytoplasmic markers. Duplicate samples of cytoplasmic (Cyto) and nuclear (Nuc) extracts were analyzed for lamin B and β-tubulin by Western immunoblotting. Molecular mass markers are indicated on the left (in kilodaltons). β-Tubulin is primarily localized to the cytoplasmic lysates. (B) RSV increases p100 processing and nuclear translocation of p52. The top panel shows a Western immunoblot of 50 μg of NEs prepared from RSV-infected A549 cells for various time periods and probed with anti-p52 monoclonal antibody. The location of unprocessed 100-kDa (p100) and 52-kDa (p52) NF-κB2 are indicated on the right. The first lane shows the molecular mass standards. The apparent sizes (in kilodaltons) are given on the left. In the bottom panel, the blot was probed with β-actin as a loading control. The experiment was repeated more than three times with similar results. (C) Time course of RSV-induced increase in Rel B nuclear translocation. Western immunoblots of 50 μg of cytoplasmic extract or sucrose cushion-purified NE from untreated or RSV-treated A549 cells were probed with anti-Rel B antibody (top panel). The blot was probed with β-actin (bottom panel) as a loading control.