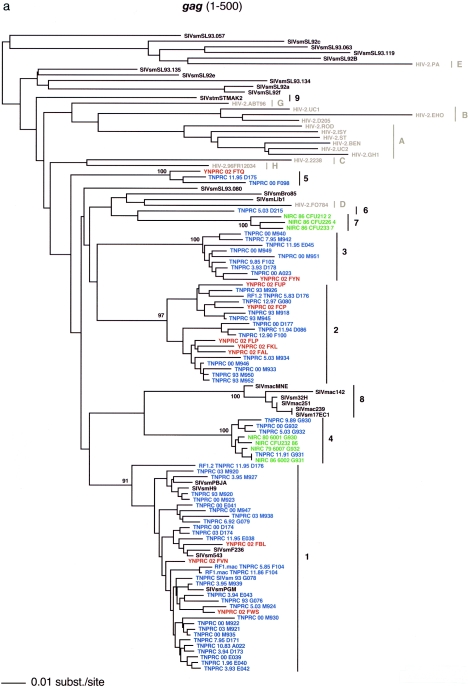
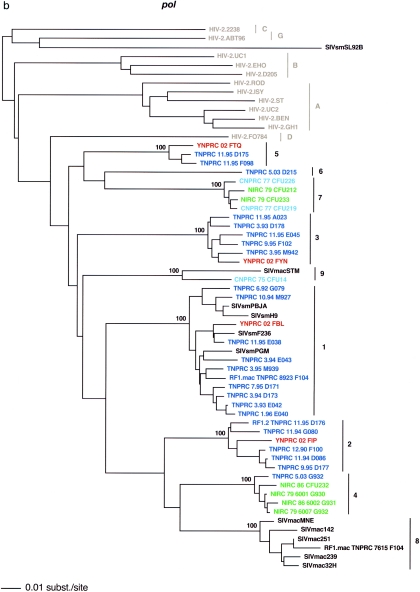
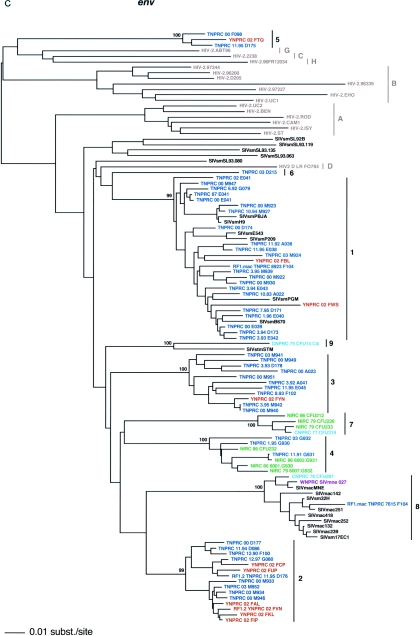
FIG. 1.
SIVsm diversity in SM colonies from four primate centers in the United States. Lineages are clusters of SIVs that are highly related and branch together. Newly characterized strains are color coded (blue, TNPRC; red, YNPRC; green, NIRC; pink, CNPRC). Lineage 1 contains the previously reported strains SIVsmB670, SIVsmPBj, SIVsm236/660/543-3, and SIVsmPGM (http://hiv-web.lanl.gov). Reference SIVsm strains and strains from wild-caught SMs are shown in black, whereas HIV-2 strains are shown in light gray. Lineages 8 and 9 include strains isolated from different species of macaques that were experimentally or accidentally infected. The trees are based on gag (500 bp) (a), pol (592 bp) (b), and env (405 bp) (c) fragments after gap-containing sites were removed. The phylogenetic trees were estimated by the neighbor-joining method using amino acid sequences. The reliability was estimated from 1,000 bootstrap replicates; only bootstrap values relevant for lineage definition are shown. Bars, number of amino acid replacements (0.01) per site. The strain nomenclature includes the assigned lineage, the primate center of origin, the year of strain collection, and the monkey identification number.