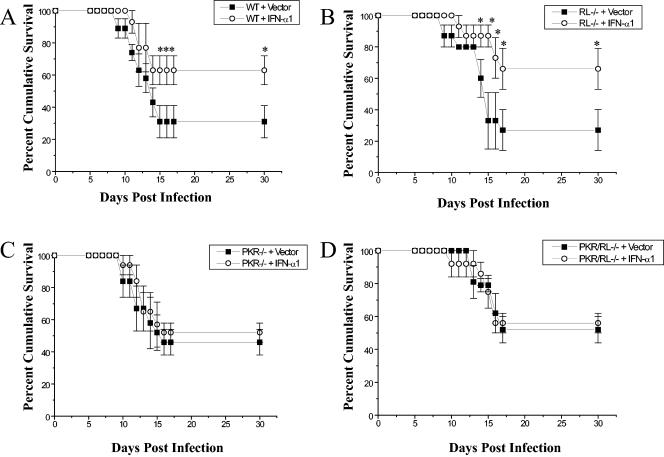
FIG. 2.
PKR is required for IFN-α1 transgene efficacy against genital HSV-2 infection. (A) Depo-Provera-treated female C57BL/6 mice (WT) (n = 15 to 20 mice/group) were intravaginally administered 100 μg of plasmid vector DNA alone (Vector) or plasmid containing the IFN-α1 transgene (IFN-α1). Twenty-four hours posttreatment, the mice were intravaginally infected with 2,400 PFU of HSV-2/mouse and monitored for survival. This figure is a summary of results of four experiments (n = 4 to 5 mice/group/experiment). (B) Conditions were the same as for panel A except that mice deficient in RNase L (RL−/−) (n = 15/group from three experiments) were employed. (C) Conditions were the same as for panel A except that mice deficient in PKR (PKR−/−) were evaluated (n = 13 from three experiments). (D) Conditions were the same as for panel A except that mice deficient in both RNase L and PKR (PKR/RL−/−) (n = 10 to 15/group from three experiments) were surveyed. *, P < 0.05 comparing the IFN-α1 transgene- to vector-transfected mice, as determined by the nonparametric Mann-Whitney rank order test.