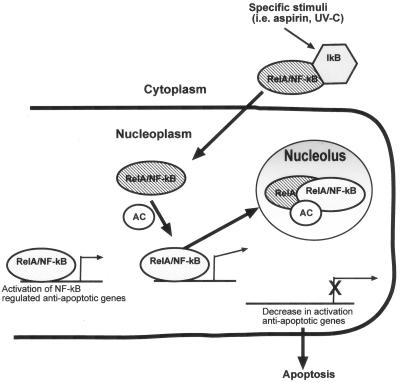
FIG. 11.
A model for the compartmental modulation of NF-κB transcriptional activity and apoptosis. In nonstimulated tumor cells, there are two pools of NF-κB, an inducible cytoplasmic pool and a basal pool that drives the transcription of antiapoptotic genes. Upon induction by aspirin, UV-C radiation, serum deprivation, and similar stimuli, inducible RelA/NF-κB complexes translocate into the nucleus, recruiting an additional cofactor (AC) to the basal pool. The induced RelA/cofactor complex does not activate transcription but complexes with basal RelA/NF-κB, and then all nuclear RelA translocates to the nucleolus. Once in the nucleolus, RelA is in a physical location different from that of its target promoters, resulting in a decrease in transcription of antiapoptotic genes and, consequently, apoptosis.