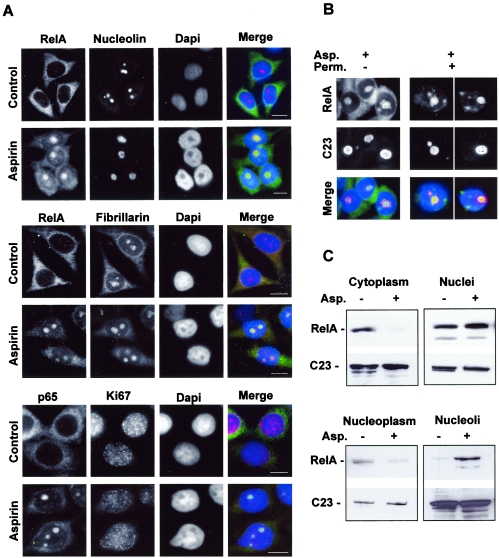
FIG. 2.
RelA localizes in the nucleolus in response to aspirin. (A) Immunocytochemical staining (magnification, ×63) showing that RelA colocalizes with the nucleolar proteins nucleolin and fibrillarin, but not with Ki67, when induced by aspirin. SW480 cells were unstimulated (control) or stimulated with aspirin (5 mM, 16 h) and then fixed, and immunocytochemistry was performed using the specified antibodies. DNA is stained by DAPI. Bars, 10 μm. (B) RelA is held within nucleolar bodies after aspirin treatment. The immunomicrographs (magnification, ×63) show the cellular localization of RelA in aspirin (Asp.)-treated (5 mM, 16 h) SW480 cells with (+) and without (−) permeabilization (Perm.) prior to fixation and immunocytochemical analysis. Nucleolin (C23) staining depicts nucleoli. Merged image shows DAPI-stained DNA (blue). (C) Aspirin induces a decrease in nucleoplasmic and an increase in nucleolar levels of RelA. Nontreated and aspirin (Asp.)-treated (5 mM, 16 h) SW480 cells were fractionated using sucrose gradients. Western blot analysis was then performed on protein extracted from the specified cell fractions using anti-RelA followed by anti-nucleolin (C23) antibodies.