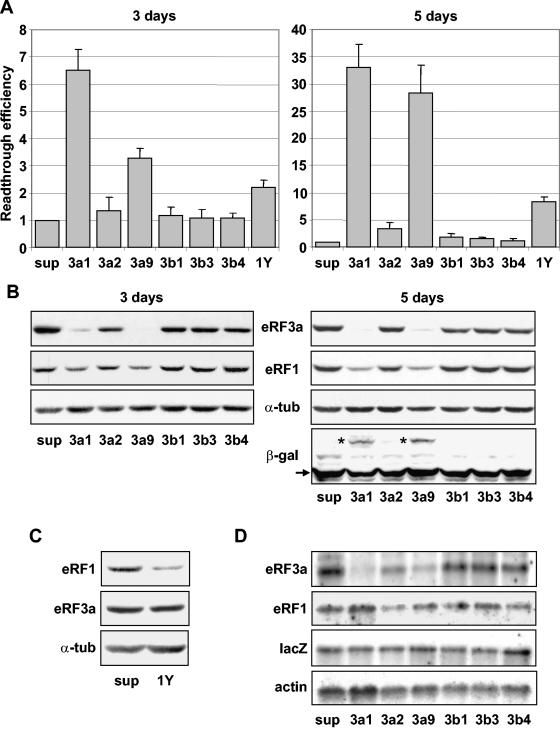
FIG. 3.
Effects of siRNAs on stop codon readthrough. 559C cells stably expressing a lacZ gene containing a premature UAG stop codon were electroporated with the empty vector pSuper (sup) or with pSuper derivatives expressing siRNAs directed against eRF3a (3a1, 3a2, and 3a9), eRF3b (3b1, 3b3, and 3b4), or eRF1 (1Y). Cell extracts performed 3 or 5 days after electroporation, as indicated, were used for β-galactosidase assays and Western blot and Northern blot analyses. (A) Readthrough efficiencies of siRNAs were calculated by dividing the β-galactosidase activity in each sample by the β-galactosidase activity in pSuper-electroporated cell extract. The results were expressed as the mean of five experiments; the error bars show the standard errors of the mean. (B) Western blot analysis performed 3 or 5 days after electroporation of cells with the plasmids described above, using anti-eRF3a, anti-eRF1, anti-β-galactosidase (only shown for 5-day electroporation), or anti-α-tubulin antibodies as indicated. The positions of the truncated and full-length β-galactosidase are indicated by the arrow and asterisks, respectively. (C) Western blot analysis performed 5 days after electroporation of cells with pSuper (sup) or plasmid expressing siRNA directed against eRF1 (1Y), using anti-eRF1, anti-eRF3a, or anti-α-tubulin (α-tub) antibodies as indicated. (D) Northern blot analysis performed 5 days after electroporation of cells with the plasmids described above. The membrane was probed successively with eRF3a, eRF1, lacZ, and actin probes as indicated.