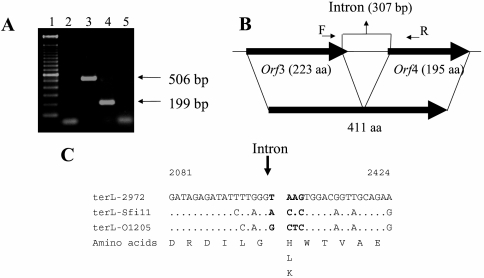
FIG. 8.
Characterization of the intron between the genes coding for the terminase large subunit of phage 2972. (A) In vivo splicing of 2972 intron RNA (terminase large-subunit gene). Lane 1, 100-bp marker (Invitrogen); lane 2, negative control without DNA, cDNA, or RNA; lane 3, PCR product obtained with 2972 DNA as a template; lane 4, PCR product obtained with RNA isolated from 2972-infected S. thermophilus cells (cDNA); lane 5, PCR product (no reverse transcription) obtained with RNA isolated from 2972-infected cells. (B) Phage 2972 genomic region containing the intron and the two ORFs coding for the terminase large subunit. Large, thick arrows indicate open reading frames; the numbers of amino acids (aa) in the deduced proteins are given. Splicing of the 307-bp intron resulted in a 411-aa protein. Small arrows represent the primers used for PCR and sequencing. (C) Nucleotide sequence alignment of the regions flanking the splicing site with the corresponding intron-free regions in two other pac-type phages (Sfi11 [orf411] and O1205 [orf26]). Differences relative to the phage 2972 sequence are indicated. Vertical arrow indicates the intron insertion site. The nucleotide positions are based on the 2972 genomic sequence (GenBank accession no. AY699705).