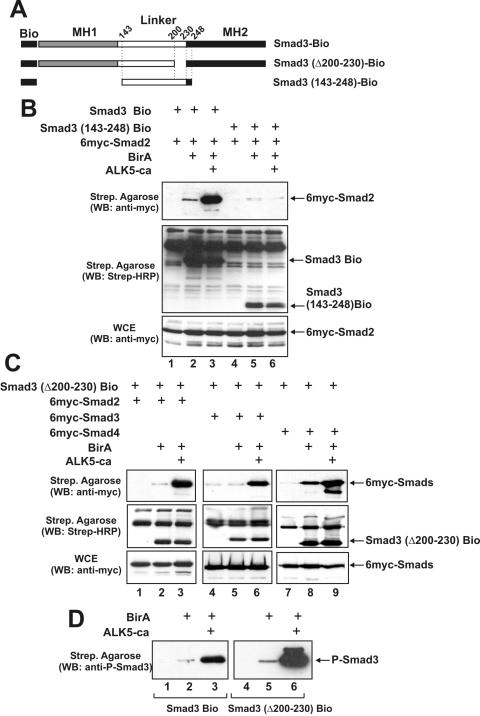
Figure 6.
Deletion of the middle region does not affect Smad homo- and hetero-oligomerization or phosphorylation by the ALK5 receptor. (A) Schematic representation of wild-type Smad3-Bio, Smad3 (Δ200–230)-Bio and the Smad3 (143–248)-Bio proteins used in the oligomerization experiments of (B and C). (B) HEK-293T cells were transfected with various combinations of expression vectors for Smad3-Bio, Smad3 (143–248)-Bio, 6myc-Smad2, BirA and ALK5-ca as indicated on top. Western blottings were performed using the anti-myc monoclonal antibody for the detection of myc-tagged Smad2 (first and third row) or HRP-conjugated streptavidin for the detection of biotinylated Smad3 proteins (second row). (C) HEK-293T cells were transfected with various combinations of expression vectors for Smad3 (Δ200–230)-Bio, 6myc-Smad2, 6myc-Smad3, 6myc-Smad4, BirA and ALK5-ca as indicated on top. Western blottings were performed using the anti-myc monoclonal antibody for the detection of myc-tagged Smad2, Smad3 and Smad4 (first and third row) or HRP-conjugated streptavidin for the detection of biotinylated Smad3 proteins (second row). (D) HEK-293T cells were transfected with expression vectors for Smad3-Bio or Smad3 (Δ200–230)-Bio in the absence or in the presence of BirA and ALK5-ca as indicated on top. Proteins bound to the streptavidin agarose beads were analyzed by immunoblotting using a polyclonal antibody recognizing only the phosphorylated form of Smad3.