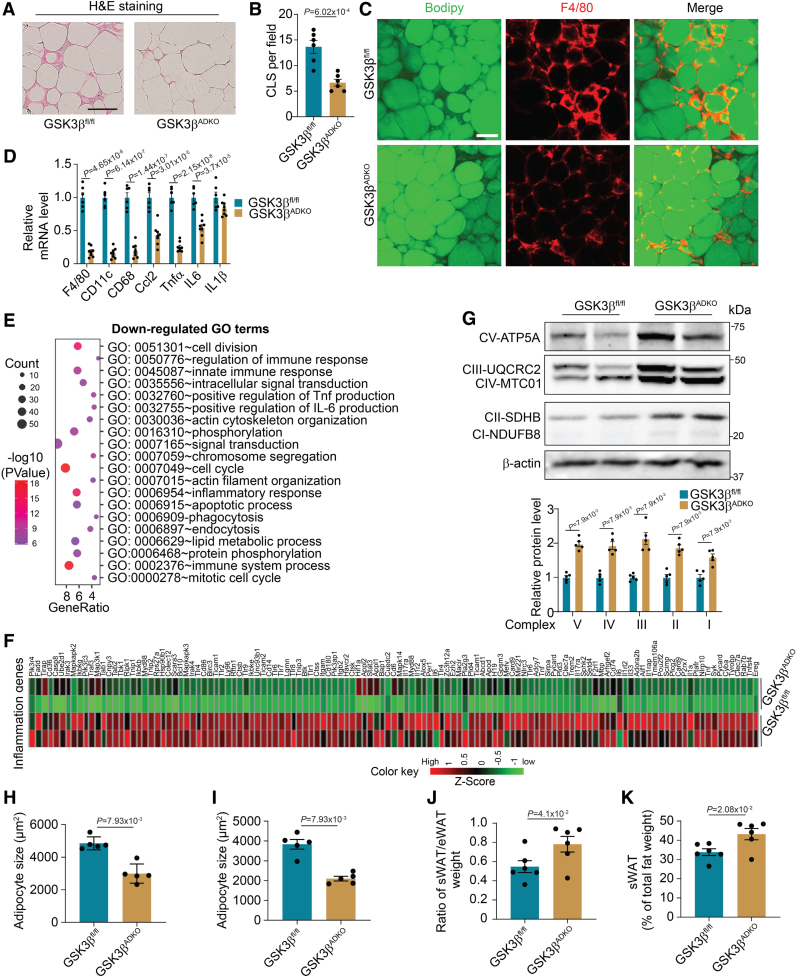
Figure 3.
Adipocyte-specific GSK3β (glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta) deficiency reduces obesity-associated adipose tissue inflammation, increases OxPhos complexes, and decreases adipocyte size. Male GSK3βfl/fl and GSK3βADKO mice were fed a high-fat diet to induce obesity and used for the experiments. A through D, Hematoxylin and eosin staining of epididymal white adipose tissue (eWAT; A), quantification of crown-like structures (CLS; B; n=6), and F4/80 staining (red) of eWAT sections (C). Lipids were stained green using BODIPY to indicate adipocytes (C), and the expression levels of inflammation-associated genes in eWAT were determined using reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (D; n=6 for GSK3βfl/fl and n=8 for GSK3βADKO). E, Gene ontology (GO) term analysis of RNA sequencing data showing downregulated gene signatures in the eWAT of obese GSK3βADKO vs obese control GSK3βfl/fl mice. F, Heat map of expression values (Z score) for inflammation-associated genes in eWAT from the indicated obese mice. G, Western blotting images of oxidative phosphorylation (OxPhos) complexes and quantification using ImageJ software (n=5). H and I, Comparison of average adipocyte sizes measured as the adipocyte area of eWAT (H) and subcutaneous white adipose tissue (sWAT; I) from obese GSK3βfl/fl and GSK3βADKO mice (n=5). J and K, The ratio of sWAT to eWAT weight (J) and the percentage of sWAT weight in total fat weight (K) of male obese GSK3βfl/fl and GSK3βADKO mice (n=6). Scale bar=100 µm. B, D, J, and K, Two-tailed unpaired t test; G through I, nonparametric test.